This article examines in dynamics the level of air pollution in a large city of republican significance in Kazakhstan — Almaty, from 2010 to 2021. The problem of air pollution in the city is very acute, emissions from stationary and mobile sources, combined with the physical, geographical and climatic features of the area, lead to a high concentration of pollutants in the city air, negatively affecting the health of the population of Almaty.
Key words: air pollution, city air, Almaty.
The indicator of atmospheric air quality in urban settlements characterizes the state of the environment in terms of atmospheric air quality and the negative impact of elevated concentrations of pollutants on the population.
Elevated concentrations of pollutants in the surface layer of the atmosphere have a diverse negative impact on human health, vegetation and soil. There is a lot of data on the negative impact on humans of carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ozone present in the atmospheric air [1, 2].
Air pollution is one of the most serious environmental factors affecting the health of any person living in low-, middle- and high-income countries.
Globally, outdoor air pollution in both urban and rural areas is estimated to be responsible for 4.2 million premature deaths per year in 2016; this mortality was due to exposure to fine suspended particles up to 2.5 μm in diameter (PM2.5), which cause cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, as well as cancer [3].
Almaty is the largest city of republican significance in the Republic of Kazakhstan. The total population as of the beginning of 2021 was 2,025 thousand people. The city has 8 administrative districts, and the highest population density compared to other cities of the republic (Table 1).
Table 1
Population density in Almaty, people per sq. km
|
Districts of Almaty |
Territory, sq. km |
2010 |
2015 |
2021 |
|
Almaty city |
683,5 |
2 034,5 |
2 401,5 |
2 895,0 |
|
Alatau |
104,1 |
1 509,2 |
1 876,5 |
2 879,6 |
|
Almaly |
18,4 |
10 230,7 |
11 134,7 |
12 025,1 |
|
Auezov |
23,6 |
12 504,9 |
11 751,6 |
13 120,3 |
|
Bostandyk |
99,4 |
2 734,1 |
3 179,3 |
3 678,3 |
|
Zhetisu |
39,5 |
3 405,8 |
4 000,0 |
4 372,9 |
|
Medeu |
253,4 |
643,5 |
745,5 |
858,2 |
|
Nauryzbay |
69,7 |
- |
1 308,1 |
2 186,5 |
|
Turksib |
75,4 |
2 397,5 |
2 782,3 |
3 241,7 |
At the present stage, the boundaries of the city and the suburban area of Almaty have expanded significantly, absorbing a number of surrounding suburban villages, as a result of which, in the vicinity of the city, fields and orchards have been reduced to a minimum. Therefore, the land around the city has largely been transformed into private sector areas built up with residential buildings.
The urbanized landscapes of the foothills of the Zailiysky Alatau are one of the main objects of air pollution in Almaty. Air pollution in Almaty is an acute environmental problem, which is aggravated by natural-climatic and physical-geographical conditions. The main ingredients of air pollution are dust, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, phenol and formaldehyde. Air pollution by carbon oxides is hazard class 4 and exceeds MPC by several times.
It should be noted that it is carbon dioxide that is a greenhouse gas that creates a screen in the atmosphere that delays infrared radiation, which as a result heats the Earth's surface. The atmosphere containing greenhouse gases is opaque to radiation, as a result of which the surface temperature rises significantly. According to the results of recent studies, the rate of warming in the republic is one and a half and two and a half times higher than the global ones, so the problem of reducing the greenhouse effect and adapting to the conditions of global climate change in a large urban area of the city and suburbs of Almaty is very relevant.
Numerous facilities are located on the territory of the city of Almaty, such as chemical plants, thermal power networks, building materials plants, boiler houses, local and food industries, in the suburbs and in private sectors of the city of furnace heating, etc.
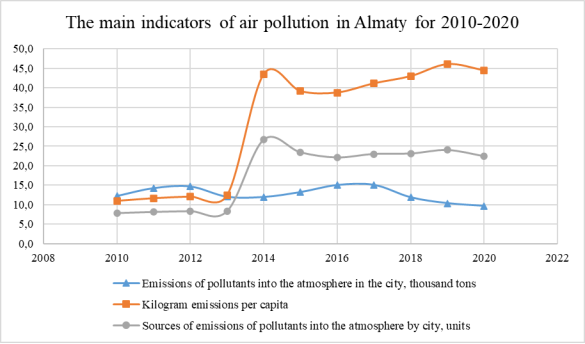
Fig. 1. The main indicators of air pollution in Almaty for 2010–2020
Along with the large heat and power complexes CHPP-1 and CHPP-2, the private sector burns mostly dirty fuels (coal, fuel oil, etc.), having low chimneys, makes a significant contribution to the air pollution of the city, which, even without it, have a high background contamination (Figure 1). A significant amount of fuel is burned by automobiles. Along with the large thermal power plants CHPP-1 and CHPP-2, the private sector burns mostly dirty fuels (coal, fuel oil, etc.), having low chimneys, make a significant contribution to the air pollution of the city, which and without it, they have high background pollution (Figure 1). A significant amount of fuel is burned by road, rail and air transport.
The situation with industrial waste remains extremely unsatisfactory. The measures taken so far do not bring us closer to the standards of developed countries. The atmospheric air is especially polluted by greenhouse gas emissions and carbon dioxide. The largest contribution to the volume of CO 2 emissions is made by energy, and from energy carriers — coal. Emissions from the thermal power complex CHPP-2, located near the western border of the city of Almaty, have a significant impact on the overall air pollution. Table 1 shows the dynamics of emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere of the city by its districts, rail and air transport.
The situation with industrial waste remains extremely unsatisfactory. The measures taken so far do not bring us closer to the standards of developed countries. The atmospheric air is especially polluted by greenhouse gas emissions and carbon dioxide. The largest contribution to the volume of CO 2 emissions is made by energy, and from energy carriers — coal. Emissions from the thermal power complex CHPP-2, located near the western border of the city of Almaty, have a significant impact on the overall air pollution. Table 2 shows the dynamics of emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere of the city by its districts.
Table 2
Emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere by districts of the city of Almaty [4, 5]
|
Districts of a Almaty |
Years | ||
|
2010 |
2015 |
2020 | |
|
Almaty city |
10 966 |
39 130 |
44 467 |
|
Alatau |
234 |
30 763 |
38 384 |
|
Almaly |
720 |
526 |
290 |
|
Auezov |
5 628 |
1 195 |
846 |
|
Bostandyk |
430 |
761 |
970 |
|
Zhetisu |
1 812 |
2 621 |
1 666 |
|
Medeu |
574 |
769 |
376 |
|
Nauryzbay |
237 |
252 | |
|
Turksib |
1 568 |
2 258 |
1 683 |
The main causes of atmospheric air pollution in the city from stationary sources are: outdated technologies of many industries; insufficient number and low efficiency of existing dust and gas cleaning plants; violations of the technological mode of operation; the use of low-quality coals in the energy sector.
To reduce emissions of harmful substances into the atmospheric air, it is necessary to install gas cleaning facilities at thermal power plants (emulsifiers for CHPP-1 and CHPP-2), in the future it is necessary to switch to natural gas; complete gasification of the private sector; the use of highly efficient dust and gas cleaning equipment at the enterprises of the city; removal of large air polluting enterprises outside the city.
References:
- Ibragimov V. R., Agishev T.Kh. Methodology for assessing the health status of the population // Fundamental research. — 2004. — No. 5. — P. 109–110; URL: https://fundamental-research.ru/ru/article/view?id=5923
- On approval of the Methodology for the formation of indicators of environmental statistics. Acting order Chairman of the Statistics Committee of the Ministry of National Economy of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 25, 2015 No. 223. Registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan on January 26, 2016 No. 12931. https://adilet.zan.kz/rus/docs/V1500012931
- Air Pollution/ World Health Organization Global Website. https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health
- Emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere by districts of the city of Almaty for 2010, 2015 and 2020 [Environmental protection in the city of Almaty for 2010–2015. Statistical compendium / in Kazakh and Russian / 30 pages. Department of the Bureau of National Statistics of the Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan for the city of Almaty.
- Environmental protection in the city of Almaty for 2016–2020. Statistical compendium / in Kazakh and Russian / 30 pages Department of the Bureau of National Statistics of the Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan for the city of Almaty

