It is proved in the article that sustainable development of administrative territory depends on the level of socio-ecologo-economic balance. Theoretical and methodological approaches to ecologically oriented administrative territory management system forming are developed. Methodological recommendations for determination of integral index of socio-ecologo-economic development of the territory are proposed. Indices of social, economic, and ecological development and integral index in Sumy region are calculated. Three-sector model of economic growth of the region, which is based on the integral index of socio-ecologo-economic development of the territory, is formed.
Key words: ecologically oriented management system, administrative-territorial entity,social development index, ecological state index, economic development index,three-sector model of economic growth.
INTRODUCTION
In spite of the constant increase of the attention to the environmental protection issues, their topicality does not decrease. Practically all world countries, regardless of their social and economic development, are to make a decision on socio-economic and ecological problems overcoming.
In recent years scientific works, considering an influence of social production on the environmental situation and how ecology influences on the level of economic development, appear increasingly.
At the same time, not enough attention is paid to the issues of the economy, ecology, and social sphere development optimality in the context of sustainable development. It means that Gross Domestic Product growth should be provided by the harmonious development of the socio-ecologo-economic system constituents and ecological parameters complex has to be taken into account in the process of managerial decision-making. Ecologically oriented territory management system forming can be a means of the sustainable development ensuring.
An importance of the ecological imperative introduction to the structure of the social and economic development management has been considered by: I. K. Bystryakov, E. A. Meyerson, and T. M. Karyakina. Works of A. S. Burtseva are devoted to the issues of ecologically oriented managerial decisions improvement. S. V. Markin, P. M. Petrenko, B. V. Yaschenko were occupied peculiarly with issues of ecologically oriented management system development at the enterprises. These issues are considered also in the works of K. G. Hoffmann, O. P. Buramtova, O. A. Lyapina, V. M. Sydorenko, V. I. Gurman, Ye. V. Ryumina, O. F. Balatskiy, etc. Works of the following foreign scientists are reflected in the context of social and economic modelling: X. Zolotas, S. Miller, M. Weber, W. Bart, M. C. Farmer, S. Lambrecht, J.-P. Vidal, J.Woo, etc.
At the same time, issues of ecologically oriented administrative territory management system forming, in terms of ensuring ecological safety, need further research.
PROBLEM STATEMENT
The objective of the research is the development of the scientific and methodological approaches to the ecologically oriented territory management system forming, which should provide harmonious functioning of socio-ecologo-economic system of the region in the conditions of natural environment conservation, life quality improvement, and economy growth rates increase.
RESEARCH RESULTS
For today, in Ukraine, as well as in most of the world countries, administrative-territorial management system functioning does not provide ecologically sustainable growth.
There are different approaches to the estimation of the countries development according to social, economic, and ecological characteristics.
Thus, Russian scientist S. O. Stepanov investigated and summarized international indices and indicators. The author proposed definition of “composite index of the country’s activity on ensuring of decent living and free human development”. At that, the initial values of this index were the following parameters: human potential development index; Gini coefficient; economic freedom index; cost of living indicator; ecological efficiency index; general death rate; democracy index; education expenses; corruption perception index. These indices are positions conglomerate, determined by socio-economic, political, and cultural conditions and factors.
Composite index calculations of the country's activity are carried out by the author by 187 countries. The first group includes the following countries of the world community: UAE, Sweden, Iceland, New Zealand, Taiwan, Austria, Finland, Denmark, Norway, Luxemburg, the Netherlands, Canada, Germany, Ireland, Belgium, Australia, France, Great Britain, Switzerland, Cyprus, Slovenia, Estonia, the Solomon Islands, and Malta. The world rating is enclosed by Burkina Faso, Turkmenistan, Syria, Laos, Iraq, Haiti, Angola, Guinea-Bissau, Afghanistan, and North Korea [3].
According to this index, Ukraine takes the 84th place in the world countries rating. At that, according to this index constituents, namely, according to economic freedom index, general death rate, corruption perception index, and ecological efficiency index, Ukraine takes the last places.
There are also other indices, reflecting socio-ecologo-economic state of the country. Thus, society sustainability index, which was developed at the initiative of Dutch researchers Geurt van de Kerk and Arthur Manuel under the aegis of Sustainable Society Fund in 2006, measures country’s achievements from the point of view of civil development sustainability by the scale form 0 (the least sustainability rate) to 10 (the highest sustainability rate).
Society sustainability index consists of indices, characterizing human well-being, ecological well-being, and economic well-being [4].
According to the society sustainability index, in 2012 Ukraine took 102nd place among 150 world countries. One of important constituents of society sustainability index is ecological one.
In this aspect, it is reasonable to mention that the highest ratings belong to the model of economic growth, functioning in Sweden.
Characteristic feature of the modern social and economic development of Ukraine is general worsening of the ecological state of the natural environment. One of the main directions, securing ecologically balanced development of the country is introduction of the ecologically oriented territory management system. Most of the scientists don’t have common opinion in respect of the essence and constituents of the whole system. Thus, some scientists define ecologically oriented management system first of all as ecological aspect of the territory functioning and ecologically safe modern economy management itself.
The essence of notion of ecologically oriented management system is investigated on the basis of the existent definitions summarizing in this sphere, table 1.
Table 1
Scientific approaches to the determination of the ecologically oriented management system essence and its structural elements
|
Author, definition |
Essence |
Fundamental constituents |
Structural elements |
|
G. G. Uvarova Ecologically oriented management [8] |
Ecologically safe modern economy management, first of all production, processes management of ecological state changes in the context of society, country, region, city, district, or enterprise. It is based on the estimation of the boundary load on the environment, determination of the necessary and allowable economic growth rates and environmental capacity to renew its properties |
Estimation of the boundary load on the environment, determination of the necessary and allowable economic growth rates and environmental capacity to renew its properties |
Ecologically safe economy, enterprise management, ecological processes management of ecological state of society, country, region, city, district, or enterprise |
|
A. A. Sadekov Ecologically oriented management[10] |
It forms and stimulates enterprise resources flows for economic objectives achievement, which are interrelated with the objectives of rational environmental management and ecologically sustainable development. It is based on the principles of the rational environmental management |
Rational environmental management |
Interrelations between economic objectives and objectives of rational environmental management and ecologically sustainable development |
|
I. L. Reshetnikova Ecologically oriented management of mercantile business[13,p. 44] |
A part of generalmanagement system, the aim of which is statedeconomic objectives achievement of commercial processes ensuring with adherence to economy principles of environmental management and environmental protection |
Adherence to economy principles of environmental management and environmental protection |
Commercial processes with adherence to economy principles of environmental management and environmental protection |
|
V. O. Lukianykhin, M. M. Petrushenko Ecologically oriented management[11] |
Purposeful influence of management system of the enterprise on its external and internal organizational processes with the help of social and technical methods system for the purpose of environment improving |
Environment improving |
Systems of social and technical methods, functioning in the context of environment improving |
|
V. Ya. Shevchuk Ecologically oriented management [12] |
System constituent of general management system, having for an object ecological policy performance and ecological objectives achievement and containing organizational structure, activities on planning, functional duties, responsibility, methodologies and methods, procedures and resources, and professionally trained human resource |
Ecological policy performance and ecological objectives achievement |
Organizational structure, activities on planning, functional duties, responsibility, methodologies and methods, procedures and resources, and professionally trained human resource |
|
O. M. Tur Ecologically oriented development[9] |
Development, furthering establishment of the optimal parameters of socio-ecologo-economic system, not threatening its integrity and creating possibilities for dynamic development and adjustment between society problems and natural environment limits. Such development should ensure preservation of assimilation potential of natural environment for present and future human generations |
Adjustment between society needs and natural environment limits; preservation of assimilation potential of natural environment for present and future human generations |
Parameters of socio-ecologo-economic system |
|
B. V. Yaschenko Management system ecologization[14,p.6] |
Process of managerial decisions-making, which through the functions of forecasting, planning, organization, operating regulation, control, and economic analysis, ensure ecological safety demands. Management system ecologization provides creation of ecologically oriented management structure, ecologization of the management functions and economic relations between subdivisions and the enterprise |
Ecological safety demands ensuring, ecologically oriented management structure, ecologization of the management functions and economic relations between subdivisions |
Functions of forecasting, planning, organization, operating regulation, control, and economic analysis, ensuring ecological safety demands |
Analysis of the existent approaches to the determination of the essence of ecologically oriented management system and its structural elements permits to make the following conclusions. Most of the authors distinguish such objectives of ecologically oriented management system as rational environmental management and natural environment protection, coherence of ecological and economic objectives, and ecological safety demands ensuring. Some authors propose to achieve the above-mentioned objectives through the estimation of the boundary load on the environment, determination of optimal economic growth rates and capacity of the environment to renew its properties, determination of the relation between ecological expenses and financial results, creation of the ecologically oriented management structure, ecologization of management functions and economic relations between subdivisions. An analysis of the existing approaches to the definition of the ecologically oriented management system permits to formulate author’s definition of this notion.
Thus, ecologically oriented administrative territory management system is regarded as purposeful influence of the administrative-territorial management bodies on the organizational processes by means of economic, social, financial, and psychological methods on the basis of ecologically oriented managerial decisions-making for the purpose of territory sustainable development ensuring.
According to the systems approach, it is expedient to consider ecologically oriented administrative territory management forming at the base level, at the level of administrative districts and regions.
Structurally, the system of ecologically oriented management considerably depends on the level of socio-ecologo-economic balance of the territory. For determination of the socio-ecologo-economic balance level, we suggest integral index of socio-ecologo-economic territory development. This index takes into account the level of social and economic development and ecological territory state, figure 1
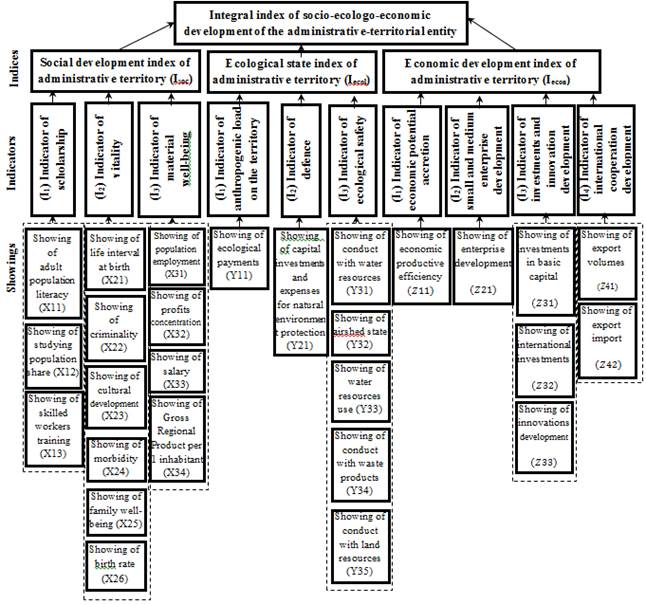
Fig. 1 . Constituents of integral index of socio-ecologo-economic administrative territory development
It is proposed to determine socio-ecologo-economic development index in the following way, table
Table 2
Determination of integral index of socio-ecologo-economic development of the territory
|
Indicators of social development |
Indicators of ecological state |
Indicators of economic development | |||
|
Indicators stimulants |
Indicators destimulants |
Indicators stimulants |
Indicators destimulants |
Indicators stimulants |
Indicators destimulants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
where xij — standardized indicators of j-th territory social state;
|
where
|
where
| |||
|
Social development index |
Ecological state index |
Economic development index | |||
|
Іsoc = |
Іecol= |
Іecon = | |||
|
Іceed = | |||||
Calculations of integral index of the socio-ecologo-economic territory development are based on the comparison of the indicators of administrative-territorial entities with their reference value.
For the purpose of systems and complex analysis of administrative territory development, it is considered to be expedient to carry out calculations of integral index of socio-ecologo-economic development according to the groups of the same types of administrative-territorial entities, differentiated according to the population density, table 3
Table 3
Regions distribution according to the level of population density
|
№ |
Regions |
Population density (pers./ km2) |
Regions |
Population density (pers./ km2) |
Regions |
Population density (pers./ km2) |
|
Groups according to the level of population density | ||||||
|
І group (Іint1) High level |
ІІ group (Іint2) Medium level |
ІІІ group (Іint3) Low level | ||||
|
1 |
Donetsk region |
166.0 |
Ternopil region |
78.2 |
Rivne region |
57.6 |
|
2 |
Lviv region |
116.4 |
75.3 |
Volyn region |
51.6 | |
|
3 |
Chernivtsi region |
111.8 |
Odesa region |
71.7 |
Poltava region |
51.4 |
|
4 |
Dnipropetrovsk region |
104.0 |
Zaporizhzhia region |
65.9 |
Sumy region |
48.4 |
|
5 |
Ivano-Frankivsk region |
99.1 |
Khmelnytsky region |
64.0 |
Mykolaiv region |
47.9 |
|
6 |
Zakarpattya region |
98.1 |
Vinnytsia region |
61.7 |
Zhytomyr region |
42.7 |
|
7 |
Kharkiv region |
87.3 |
Kyiv region |
61.1 |
Kirovohrad region |
40.8 |
|
8 |
Luhansk region |
85.2 |
Cherkasy region |
61.1 |
Kherson region |
38.1 |
|
9 |
Kyiv city |
3368 |
Chernihiv region |
34.1 | ||
|
10 |
Sevastopol city |
441.4 | ||||
For more objective assessment of the socio-ecologo-economic administrative territory development state, it is proposed to form three groups of the territories according to the level of population density; accordingly, calculations of the integral index were carried out for each group.
The calculations of the socio-ecologo-economic administrative territory development rate by the example of Sumy region in 2009 showed the following results: social development index is 0.78, ecological development index — 0.45, economic development index — 0.59, integral index of socio-ecologo-economic development is 0.59.
For determination of integral index of socio-ecologo-economic administrative territory development, graphic method, according to which the level of balance is determined by the correlation of existent socio-ecologo-economic system state optimality, can be used as well, figure 2
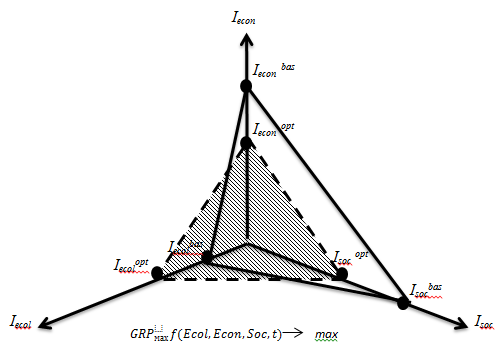
Fig. 2. Areas of socio-ecologo-economic administrative territory development
Area (Іecolbas, Іecon bas, Іsoc bas) reflects existent socio-ecologo-economic state of administrative-territorial entity. Area (Іecolopt, Іecon opt, Іsoc opt) characterizes optimal state of the territory development, ensuring maximal GRP growth.
GRP growth of administrative-territorial entity, depending on social, economic, and ecological parameters, is determined according to the models of economic growth.
Works of P. M. Romer, R. Lucas, S. Rebelo, which are based on the research results K. Arrow, H. Uzawa, E. Sheshinski, are the basis for modern neoclassic theory of economic growth there. Distinctive features of these models are distinguishing of separate sector of scientific research.
An analysis of these models shows that aggregated models of economic growth of regional economy, in which ecological factor is taken into account, are yet not enough represented in the modern scientific literature. This disadvantage partly is eliminated in the model, proposed by Ya. Ya. Vahapova [2, p.56]. This model takes into account productive, R&D sector, educational sector, ecological sector, and social sector.
In our opinion, it is expedient to unite productive and R&D sectors into integrated economic sector and to include educational sector into the social sector. Then the model of economic growth will be represented as three-sector model, table 4.
Table 4
Three-sector model of economic growth
|
Sectors |
Characteristics of the economic growth model sectors |
|
Social sector |
|
|
| |
|
Ecological sector |
|
|
| |
|
Economic sector |
|
|
|
Thus, three-sector model of economic growth looks like this:
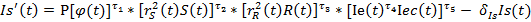
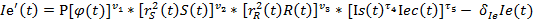
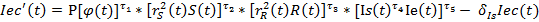
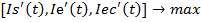
The developed model of economic growth permits to project trajectories of socio-ecologo-economic administrative territories development and to determine interrelations between its constituents.
CONCLUSIONS
Gross Domestic Product growth is provided by harmonious socio-ecologo-economic region development. Ecologically oriented management system formation is a means of ensuring the sustainable development of the territory. Ecologically oriented administrative territory management system forming foresees previous diagnosing of its socio-ecologo-economic state for evidence of its balance. For determination of socio-ecologo-economic balance level, it is proposed to use integral index of socio-ecologo-economic territory development. Integral index in its turn consists of social, ecological, and economic development indices. Integral index calculations of socio-ecologo-economic territory development are based on comparison of indicators of the separate administrative-territorial entities with their reference value.
Determination of the integral index is performed for each region of Ukraine. At that, it is expedient to perform grouping of these regions according to the level of population density. Partial and integral indices of socio-ecologo-economic development are used during forming of three-sector model of administrative territory economic growth. This model includes social, economic, and ecological sectors, each of which is described by certain set of factors.
Developed three-sector model of economic growth permits to forecast social and economic development of the territory taking into account ecological factor.
References:
1. Быстряков И. К. Социальная экология: курс лекций / И. К. Быстряков, Е. А. Меерсон, Т. Н. Карякина; под общ. ред. Е. А. Меерсон. –Волгоград: Изд-во Волгоградского государственного университета,1999. — 256 с.
2. Вагапова Я. Я. Моделирование экономического роста с учетом экологического и социального факторов / Я. Я. Вагапова. — М.: МАКС Пресс, 2007. — 128 с.
3. Степанов А. С. В поисках качества жизни / А. С. Степанов. — 2013. — URL: http://www.ng.ru/nauka/2013–04–24/12_quality.html
4. Рейтинг стран мира по уровню устойчивости общества — информация об исследовании. — URL: http://www.ssfindex.com/
5. Экологическое обоснование и стратегия природоохранной деятельности в нефтегазовом комплексе / С. В. Маркин, Е. Е. Белоусова, О. П. Лыков и др. — URL: http://www.gubkin.ru/general/programma_niu/pub/pub32.pdf
6. Балацкий О. Ф. Экологизация теплоэнергетического производства / О. Ф. Балацкий, А. М. Телиженко, Б. В. Ященко // Теплоэнергетика: внешние издержки и проблемы принятия решений: монография / под ред. О. Ф. Балацкого, А. М. Телиженко. — Сумы: Слобожанщина, 2001. — С. 396
7. Жулавський А. Ю. Проблеми екологізації системи управління адміністративно-територіального рівня. Ж. / А. Ю. Жулавський, О. О. Павленко, Ю. Т. Алібекова // Механізм регулювання економіки. — 2011. — № 4 — С. 34–39
8. Уварова Г. Г. Теоретические основы экологически ориентированного управления национальной экономикой: Дис.... канд. экон. наук: 08.00.01: Ростов н/Д, 1999 140 c.. — URL: http://www.lib.ua-ru.net/diss/cont/86789.html
9. Тур О. М. Еколого-орієнтований розвиток національної економіки: основні дефініції та принципи / О. М. Тур // Механізм регулювання економіки. — 2009. — № 1. — С. 225–237.
10. Садеков А. А. Механизмы эколого-экономического управления предприятием: монографія / А. А. Садеков. — Донецк: ДонГУЭТ им. М. Туган-Барановского, 2002. — 311 с.
11. Лукьянихин В. А., Петрушенко Н. Н. Экологический менеджмент: принципы и методы: монография / В. А. Лукьянихин, Н. Н. Петрушенко; под научн. ред. В. А. Лукьянихина. — Сумы: ИТД “Университетская книга”, 2004. — 408 с.
12. Шевчук В. Я. Екологічне управління: підручник / В. Я. Шевчук, Ю. М. Саталкін, Г. О. Білявський та ін. — К.: Либідь, 2004. — 432 с.
13. Решетнікова І. Л. Методичні підходи до еколого-орієнтованого управління торговельним підприємством // І. Л. Решетнікова / Механізм регулювання економіки. — 2009. — № 4. — С. 42–47.
14. Ященко Б. В. Екологізація управління теплоенергетичним комплексом в умовах корпоратизації: Автореф. дис... канд. екон. наук: 08.08.01. — Сум. держ. ун-т. — Суми, 2001. — 20 с.
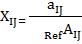
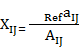
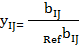
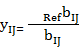
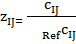
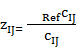
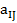 — i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory social development state;
— i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory social development state;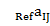 — reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing social development state
— reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing social development state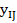 — standardized indicators of j-th territory ecological state;
— standardized indicators of j-th territory ecological state;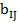 — i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory ecological state;
— i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory ecological state;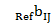 — reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing ecological state
— reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing ecological state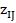 — standardized indicators of j-th territory economic state;
— standardized indicators of j-th territory economic state;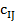 — i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory economic state;
— i-th indicator value, characterizing j-th territory economic state;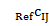 — reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing economic state
— reference value of i-th indicator, characterizing economic state


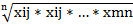
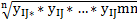
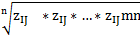
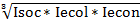
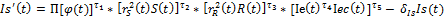
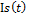 – social index, reflecting social sphere state.
– social index, reflecting social sphere state. 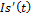 – social index growth in a unit of time.
– social index growth in a unit of time. 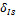 — social index decrease rate because of worsening of the social sphere state, connected with the growth of population morbidity, life interval reduction, society stratification rate increase. δ r>0; τ1, τ2 τ3, τ4 τ5 — rate parameters, 0≤ τ1≤ 1, 0≤ τ2≤ 1, 0≤ τ3≤ 1; P — scale parameter, P>0.
— social index decrease rate because of worsening of the social sphere state, connected with the growth of population morbidity, life interval reduction, society stratification rate increase. δ r>0; τ1, τ2 τ3, τ4 τ5 — rate parameters, 0≤ τ1≤ 1, 0≤ τ2≤ 1, 0≤ τ3≤ 1; P — scale parameter, P>0. 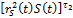 — common labour amount, which is used in social sector.
— common labour amount, which is used in social sector. 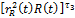 — physical capital amount, which is used in social sector.
— physical capital amount, which is used in social sector. 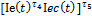 — reflects dependence of social index value from the state of surrounding environment and economic state
— reflects dependence of social index value from the state of surrounding environment and economic state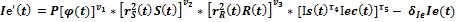
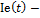 ecological index, reflecting surrounding environment state;
ecological index, reflecting surrounding environment state; 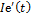 –ecological index growth, reflecting changes of surrounding environment state, taking place in a unit of time. δ θ — of ecological index decrease rates because of ecological state worsening, connected with surrounding environment pollution, δ θ>0, v1,v2,v3 — rate parameters, 0≤ v1≤ 1, 0≤ v1≤ 1, 0≤ v3≤ 1, Е — scale parameter, Е>0.
–ecological index growth, reflecting changes of surrounding environment state, taking place in a unit of time. δ θ — of ecological index decrease rates because of ecological state worsening, connected with surrounding environment pollution, δ θ>0, v1,v2,v3 — rate parameters, 0≤ v1≤ 1, 0≤ v1≤ 1, 0≤ v3≤ 1, Е — scale parameter, Е>0.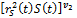 – common labour amount in the ecological sector, in product
– common labour amount in the ecological sector, in product 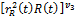 — physical capital amount, which is used in ecological sector.
— physical capital amount, which is used in ecological sector.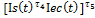 — reflects dependence of ecological index value on the state of social environment and economic condition
— reflects dependence of ecological index value on the state of social environment and economic condition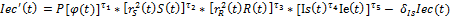
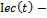 economic index, reflecting the state of productive, innovative, and investment environment.
economic index, reflecting the state of productive, innovative, and investment environment. 
