This article will discuss venture business, trends in its development in Russia and worldwide, its impact on the country's economy, as well as venture investments. This is the age of scientific progress; new technologies that can change the life of mankind are constantly emerging, so a business that promotes these technologies is very important. However, the development of such a business has its challenges, which will also be discussed.
Keywords: innovative technology, profits, risks, venture investments, venture capital market.
The experience of developed countries shows that venture entrepreneurship has become crucial part of any economy, also in terms of support of scientific and technological progress.
Experts say that venture capital has become a mechanism that allows to implement innovations at the most critical stages of their development and commercialization, where other mechanisms do not always work.
Venture capital, combining different forms of capital (equity, loan, and entrepreneurial capital) can be considered as an intermediary in economic relations between investors and companies, which are in need of financing [2].
We can say, that in real life, venture capital investments meet global trends in scientific and technological innovations and are considered effective for development of innovative companies and startups. Venture capital business is crucial when creating modern economy of the country.
Utilizing venture capital will allow developing economies to come closer to developed countries, like USA and Germany in terms of revenues in the nearest future. The greatest example is Singapore has succeeded in setting its innovation venture capital business at a high level and this has helped it to match the per capita GDP of advanced economies around the world. This was achieved largely due to the development of venture business in the country [2].
A specific feature of the venture business is the high intellectual and professional level of venture entrepreneurs and managers. Such professionals are extremely difficult to nurture. Their knowledge and experience lie at the intersection of basic and applied sciences, innovation management, and knowledge of high-tech industries.
Venture capital business started to be shaped by the government in the US in 1953. However, the philosophy and idea of creating some agency, that would help small businesses to flourish, began to arise years earlier in several other agencies, mainly as a response to the crisis, caused by the Great Depression and World War II [1]. The SBA (Small Business Administration) adopted a special law on investment in small business. The government started lending to small businesses on preferential terms. If the SBA approved a project, the government provided a soft loan for it. The credit was then also approved by the SBA [4].
Right now, the US venture capital business is very well developed. In 2021, US startups attracted a record $329.8 billion in venture capital investment, compared to $166.6 billion a year earlier [7]. This suggests that investors have shown a willingness to invest large sums in relatively young companies.
The main stages of venture capital business development in the United States of America were as follows:
- 1970s — semiconductors and biotechnology;
- 1980s — personal computers;
- 1990s — Internet (Dot-Com Boom).
In Europe, the venture business began to develop in the early 1980s. It was their advantage, because European investors could use twenty years of US experience in the industry. There is no separation between private equity funds and personal venture capital funds in Europe. This is one of the main differences between the EU and the U. S. in the venture capital business. Today, the European venture business is more focused on the real support and development of (Small and Medium-sized enterprises) SMEs.
As we already mentioned, the American experience in venture capital is largely copied by the Europeans. In 1983, the European Private Equity and Venture Capital Association (EVCA) was established as a joint initiative of the European Commission and representatives of the venture capital industry of European Union.
The EVCA helps creating favorable conditions for the development of venture capital business in European countries. Its main strategic objectives are attracting the attention of institutional investors to venture capital investments, representing its members and other venture capital industry players in European institutions, developing accessible and efficient venture capital exit mechanisms and strategies.
Overall, the venture capital market is on the rise and breaking records. Global venture investments in year 2021 totaled $643 billion. Compared to 2020 ($355 billion), it increased by 92 percent [7].
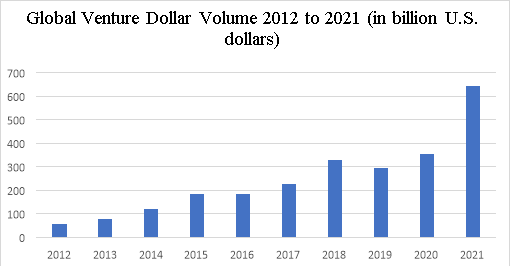
Figure 1
The venture capital business has become a highly sought-after industry, especially in Japan, South Korea, Canada, USA and many other countries in Europe.
The venture capital market in Russia is quite young. The beginning of the formation of venture entrepreneurship in Russia was in 1990. The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) was at its origins. Compared to the venture capital markets in western countries, Russia is underdeveloped, so it is yet to see its peak. That said, the industry is actively developing, and the venture capital market in Russia is keep on growing.
We should point out, that political and entrepreneurial climate favorable for venture capital investments is gradually forming in our country with each year. Several steps taken by the venture capital industry community and government contribute to the development of SMEs. These companies, in their turn, help Russian economy grow [2].
In 2021, the Russian venture capital market grew almost 3.5 times, from ₽24.9 billion to ₽85.2 billion, while the number of deals increased from 203 to 221. The market growth was driven by an increase in the average check in the «foreign investors», «private funds» and «corporate investors» segments [2]. We should mention that this happened during the crisis, which makes this growth even more impressive. This happened despite an overall decline in IT companies' revenues in 2020. However, some markets, such as the cloud technology, only keeps on growing.
The foreign investment sector showed the most significant growth. It accounted for 44 billion rubles, just over half of the total market [2].
Experience of countries comparable with Russia in the level of development shows that state intervention in innovative processes is necessary to create incentives for innovations in the private sector itself — to introduce new technologies, to enter new markets and to launch their own technological productions. For Russia, considering objective tendencies of its economy, it is more convenient to use its own scientific and technical potential, attracting foreign investments and technologies.
In this case the government support is needed when talking about crucial segments of Russian economy [5]. Some actions are already being taken (reforming higher education, creation of «special economic zones» for startups involved in creating innovations, development of innovation infrastructure). Small innovative entrepreneurship in science and technology is the most dynamic sector of innovative economy, able to respond quickly to the needs of the market of science-intensive high-tech products, to quickly rearrange their production, to effectively master the creation of knowledge-based products and services.
Innovative activity of Russian enterprises is still low, even with all the measures taken. According to the Federal State Statistics Service, only 8–9 % of enterprises are engaged in technological innovations, while in the countries with developed economies, like USA, Canada, Japan — from 71 to 82 % [7]. Thus, the innovation potential of the Russian economy, science and education system is yet to be unveiled.
The main problems holding back the development of the venture capital industry in Russia are:
— Very little presence of Russian capital on the venture capital market in Russia;
— Lack of economic incentives for attracting direct investment in high-tech enterprises, providing acceptable risk for venture investors;
— Underdeveloped infrastructure;
— Insufficient realization of specific innovation projects due to low demand for scientific and technological products.
— High level of corruption
— Sanctions
The Russian economy is currently characterized by a high degree of differentiation of regions by the level of investment attractiveness, which is associated with many factors, in particular the investment potential of the region, which is determined by the resource and raw material, personnel, production, financial security, and the level of investment risks associated with economic and political changes in the business environment. In Russia in the implementation of venture capital financing should not disperse funds over many regional programs but concentrate them on the highest priority areas [5].
It is important to rely on regions that are leaders in economic development. Currently in Russia there are several major prosperous cities (Moscow, Saint-Petersburg, Kazan, Yekaterinburg, etc.) where it makes sense to finance projects to create technology parks for the development of key areas [3].
Thus, venture business in Russia is rather underdeveloped (except for the nuclear and space spheres), mainly due to lack of sufficient funding and investment. To remedy this, the state should create specialized funds aimed at supporting innovative innovations and helping them to be promoted. The state support will allow the country to develop ventures to a certain level, which will attract foreign investors from large corporations. All this together will give a qualitative and active development of the industry in Russia.
The actions of the government of Russia are also needed to create the infrastructure to enable the creation and development of high-tech businesses [6].
Government incentives to increase interest in technology, as well as any payments and guarantees for high-tech start-ups, may help to increase the number of firms creating new technologies. Thus, entrepreneurs will feel confident in creating high-tech businesses because they will feel support. After all, many entrepreneurs start a more common business precisely because of the higher degree of risk in high-tech entrepreneurship, and state support will help level out these risks and attract investors, so that over time venture capital business in Russia will become a developed sector and people will seek to start businesses related to new technologies.
References:
- About the SBA. SBA (2022). Available at: https://proxy.www.sba.gov/about-sba/what-we-do/history (accessed 19 May 2022).
- Foreign Investment and Government Indifference: Trends in Russian Venture Capital. RBC (2022). Available at: https://trends.rbc.ru/trends/innovation/61c039b19a7947635587c04d (accessed 19 May 2022).
- Kuznetsova M. V. Ways of improving the effectiveness of innovative projects venture financing: Monograph / M. V. Kuznetsova. M.: INFRA-M, Series Scientific Thought, 2016. 102 p.
- Kuznetsova, M. V. The impact of economic sanctions on the development of venture capital industry in Russia / M. V. Kuznetsova, E. A. Pyanzina // Corporate Economics. — 2018. Pp. 16–24.
- Kuznetsova M. V. Characteristics of venture capital market / M. V. Kuznetsova // Scientific Bulletin of the Magnitogorsk branch of Russian Academy of national economy and public administration, 2014. No. 1. Pp. 183–188.
- Rodionov I., Nikkonen A. Venture capital and direct investments is in the innovation economy. The choice of venture capital sources: course of lectures. Saint-Petersburg: of venture capital, 2011. 171 p.
- What to watch for in the 2022 IPO market. PitchBook (2022). Available at: https://pitchbook.com/news/articles/2022-ipo-spac-market-vc-exits-predictions (accessed 17 May 2022).

