Introduction
Drilling fluid, often referred to as drilling mud, plays a crucial role in the oil and gas industry by facilitating the drilling process through functions such as cooling the drill bit, transporting cuttings to the surface, and maintaining wellbore stability. Among its key characteristics, filtration properties are particularly important as they determine the amount of fluid lost to the formation and the quality of the resulting filter cake, which helps prevent formation damage. This article examines the filtration properties of modern drilling fluids based on recent experimental studies and advancements in fluid compositions. Modern drilling fluids have evolved to include advanced additives, such as nanoparticles and polymers, to enhance performance under extreme conditions (such as high temperature and salinity). The focus will be on both water-based and oil-based systems, exploring how to optimize rheology and filtration behavior to minimize operational risks. For context visualization, here is an image of a drilling rig showing the contour of drilling fluid:

Fig. 1. Drilling Rigs | Tidal Petroleum
This study summarizes the results of various research efforts, highlighting innovations in fluid loss control and the impact of additives on filtration efficiency. Effective management of filtration characteristics not only reduces reservoir damage but also ensures well integrity, making it a cornerstone of modern drilling operations.
Background on Drilling Fluids
«Since the early stages of rotary drilling, drilling fluids have been used; however, modern formulas represent complex mixtures designed to meet specific well conditions. They are typically classified into water-based muds (WBM), oil-based muds (OBM), and synthetic-based muds (SBM). The main components include the base fluid, weighting agents such as barite or hematite, thickeners like bentonite or xanthan gum, and filtration control agents such as starch or polyacrylamide. Filtration performance refers to the ability of the fluid to form a thin and impermeable filter on the wellbore wall, which can minimize the invasion of fluid into porous formations. The historical evolution has progressed from simple mixtures of clay and water to modern systems using nanomaterials to improve thermal stability and reduce fluid losses. For instance, in high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) conditions, traditional drilling fluids often do not meet the requirements, leading to excessive filtration and potential wellbore collapse risks. Understanding this context is crucial for grasping the research methods applied in modern studies. Illustrating the modern components of drilling fluids can clearly demonstrate these elements:
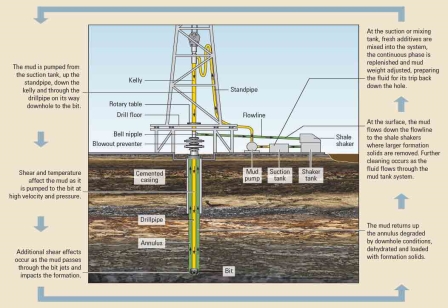
Fig. 2. The Defining Series: Drilling Fluid Basics | SLB
Filtration Properties Explained
Filtration properties are measured through parameters like fluid loss volume, filter cake thickness, and permeability. Standard tests include the API filter for low pressure and low temperature (LPLT) conditions and the HPHT filter for extreme conditions. Fluid loss occurs when the liquid phase of the drilling fluid penetrates the formation, which can lead to swelling, reduced permeability, or sealing issues. Clay forms as a result of the deposition of solid particles, serving as a barrier; ideally, it should be thin and have low permeability to effectively control this loss. In a modern context, filtration is influenced by rheological factors such as viscosity and gel strength, which affect how solid particles can form bridges within the pores of the formation. Studies show that optimizing these characteristics can reduce fluid loss by up to 50 % in complex formations. Graphs depicting filtration behavior often show cumulative fluid loss over time, highlighting the spurt loss phase followed by steady-state filtration. Here is a representative graph of filtration properties in drilling fluids:
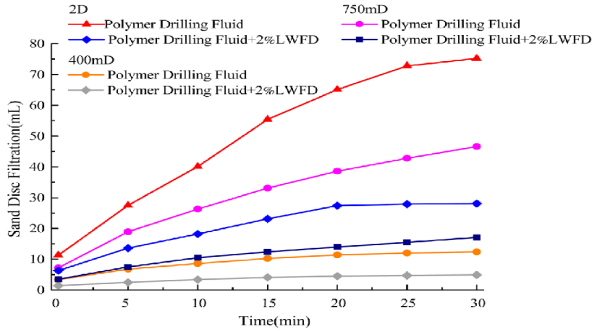
Fig. 3. The plugging property of LWFD for sand discs with different...
Modern Drilling Fluids and Their Composition
Achievements in drilling fluids focus on environmentally friendly and highly effective additives. For example, oxidized graphene modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI-GO) has been studied for water-based drilling fluids, demonstrating improved rheological stability and reduced filtration losses under saline and high-temperature conditions. Other innovations include the use of anionic nanoparticles to enhance rheological properties and filtration losses while maintaining ideal viscosity and reducing fluid losses. Natural materials are also gaining increasing interest; bone powder from cattle (CBP) has been evaluated as an additive to reduce fluid losses, showing better results compared to calcium chloride carbonate in some cases by forming denser filter cakes. Similarly, Cupressus cones powder has been tested in water-based muds, demonstrating improvements in filtration control without adversely affecting rheology. A visual of a drilling fluid filtration test apparatus helps in understanding the testing process:

Fig. 4. Drilling Mud Testing Equipment & Procedures | Physical — Drilling...
Compositions are tailored for specific challenges, such as using manganese tetroxide with bridging agents to optimize filter cake quality in weighted muds.
Experimental Investigations
Recent experimental studies employ standardized methods to assess filtration. One study investigated the rheological and filtration properties of water-based muds enhanced by various anionic nanoparticles, finding that silica nanoparticles significantly reduce fluid loss. Another examined the impact of temperature and additive concentration on filtration, using viscometers and filter presses to measure changes. In a notable experiment, PEI-GO was added to muds exposed to 200°C and high salinity, resulting in minimal fluid loss compared to base muds. Investigations also include novel additives like rice husk or date seed powder for sustainable alternatives, with tests showing comparable performance to synthetic agents. Graphs from these studies often illustrate the relationship between additive concentration and filtration volume:
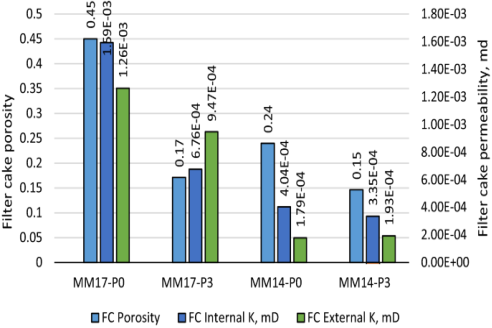
Fig. 5. Improving the filtration properties for manganese tetroxide mud...
These experiments underscore the importance of tailored formulations for specific drilling scenarios.
Results and Discussions
Results from various studies consistently show that modern additives reduce fluid loss by 20–60 %, depending on conditions. For example, during testing at high temperature and pressure (HPHT), the optimized drilling fluid formed a filter cake less than 2 mm thick, with a fluid loss of less than 10 ml every 30 minutes. The discussion emphasized trade-offs; while nanoparticles improve filtration characteristics, they can increase viscosity, requiring a delicate balance. Environmental considerations are paramount; adding biodegradable components like calcium carbonate (CBP) reduces the ecological footprint without compromising performance. Challenges include cost and scalability, but the benefits of reducing downtime justify its implementation. An additional view of drilling fluid composition aids in discussing these results:
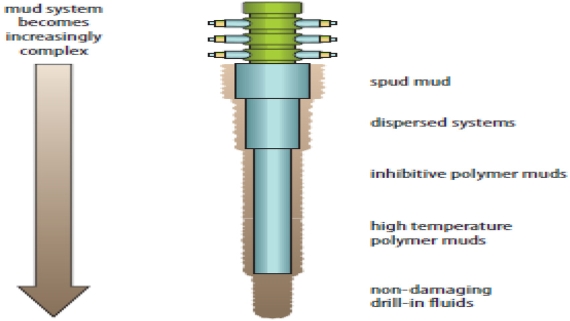
Fig. 6. Drilling Fluid Composition Requirements (Source: OGP / IPIECA...
References:
- Experimental investigation of rheological & filtration properties and... — https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0032591020303351
- An experimental investigation into the rheological behavior and... — https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2024/ra/d3ra07874d
- Rheological Behavior and Filtration of Water-Based Drilling Fluids... — https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.1c04398
- An Evaluation of the Rheological and Filtration Properties of Cow... — https://www.mdpi.com/2227–9717/13/7/2205
- An experimental investigation into the rheological behavior and... — https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10988363/
- Rheological and filtration characteristics of drilling fluids enhanced... — https://www.sciopen.com/article/10.26804/ager.2018.03.01
- Experimental study on water-based mud: investigate rheological... — https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13202–022–01471–8
- Investigation of Rheological and Filtration Properties of Water-Based... — https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315851964_
- Investigation_of_Rheological_and_Filtration_Properties_of_Water-Based_Drilling_Fluids_Using_Various_Anionic_Nanoparticles Optimizing filtration properties of water-based drilling fluids — https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927775725004923
- Improving the filtration properties for manganese tetroxide mud... — https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598–022–21897–8

