Analysis of the impact of financial costs on heat, electricity, utilities and staff showed that their reduction can significantly improve the quality of the educational process of institutions in Republic of Kazakhstan. Increased state sanitary and hygienic requirements for microclimate in educational institutions reflect the growing well-being of the population, however, at the same time this leads to increased consumption of expensive heat and electricity. Optimization of energy and resource conservation is the most important idea in the design and implementation of “smart” educational building concept. The article proposes a new design and technology for creating an individual adaptive student desk, the operation control algorithm of which significantly reduces the heat and electricity consumption in the educational building. Introduction of the proposed resource-saving technologies of workplaces increases the comfortable learning environment and reduces heat and electricity consumption in educational institutions by 30–50 percent, especially in the autumn-winter period of study.
Keywords: smart educational building, adaptive system, microclimate of student workplace, optimization of energy and heat consumption.
Introduction
Government policies to improve the quality of education require new approaches in the management of educational institutions. The most important component of the optimal organization of the educational process is to ensure a comfortable conditions and the implementation of standards for the illumination of students' workplaces. The difficult environmental situation in Almaty city and the restrictions on heat and electricity consumption stimulate educational institutions to make more efficient use of available material resources to train demanded mid-level specialists in the field of business, communications and the digital economy.
Reducing the consumption of material resources also increases the competitive advantages of private educational institutions, contributes to the growth and appropriate use of financial resources. All this improves the development prospects of the educational institution considered in the article as a modern digital adaptive institution.
The educational institutions of our country are a complex multi-link dynamic management system, which influenced by heterogeneous external factors, difficult to formalize (digitize), such as:
− multilevel initial training of future students,
− undifferentiated pay for teachers,
− spasmodic cash inflation,
− decrease in real incomes of employees and teachers,
− increase in tariffs for electricity and heat, water,
− rise in the cost of utilities, etc.
Studying the influence of heat and electricity consumption parameters using intelligent automated controllers which built on the basis of modern microcontrollers is an important advance project that allows the construction of a “smart” educational building in stages from the simple to complex principle.
Optimization based on digital systems intelligent control of energy and heat consumption in the educational building, taking into account sharp changes in natural external factors, is an important and urgent problem of the education system and will contribute to the development of Kazakhstan as a digital society.
The degree of problem understanding
At the present stage of development of architecture and the construction industry, a variety of automation systems are offered, the implementation of which contributes to the creation of a «smart» educational building.
The analysis of existing projects in the countries of the West and Russia has a high cost of their implementation in Kazakhstan and require significant investment, which can lead to a sharp increase in the cost of training and a decrease in the competitiveness of a private educational institution.
At the same time, the work on adapting educational buildings to the requirements of modern society requires the application of a “smart” educational building concept which adequate to Kazakhstan.
The conceptual definition of a “smart” educational building of a private educational institution of the Republic of Kazakhstan, in our opinion, is an environmentally friendly, comfortable for teachers and students to work, cost-effective and aesthetically beautiful building, maximally adapted to the transport and engineering infrastructure of the city, constantly progressing as an engineering structure, designed to organization of a successful and high-quality educational process for the preparation of specialists demanded by the country's economy.
The most important criteria for a smart educational building are:
− system of safety in case of emergency and protection against illegal penetration of attackers into the educational building;
− creation of optimal environmental parameters (dust, gas, temperature, humidity and percentage of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and other air parameters in accordance with the standards of the Republic of Kazakhstan) in the premises of the building in accordance with their intended purpose;
− availability of on-line system control of video surveillance, climate from a smartphone, universal remote control, panels;
− dispatching operation of all systems: air conditioning, ventilation, heating, water supply and sanitation, cleaning of premises and utilization of household waste, etc.
− providing savings from 30 % to 50 % of institution’s energy and heat resources and be recouped within 2–3 years.
In terms of climatic conditions and the level of technological development, the closest are the solutions proposed by Russian specialists. They created a set of equipment for retrofitting existing school ventilation systems with insulated air ducts that supply outdoor air to classrooms.
The remote control system allows you to manually select the fan speed, adapting the level of ventilation depending on the number of students.
An air temperature control system is also available. Built-in standard filters are able to clean the air of: dust, dirt, exhaust gases, substances that cause allergies; viral organisms, bacteria, mold colonies; industrial gases, stove smoke. The automated control system gives a warning signal when the filters are dirty and must be replaced [2, p. 1].
To place a compact ventilation unit for one classroom, a wall area of one square meter is required. Installation and launch of the system does not require large labor costs and funds, the cost of re-equipment of one classroom is 70 thousand rubles or 350 thousand tenge in November 2018 prices (see Figure 1).
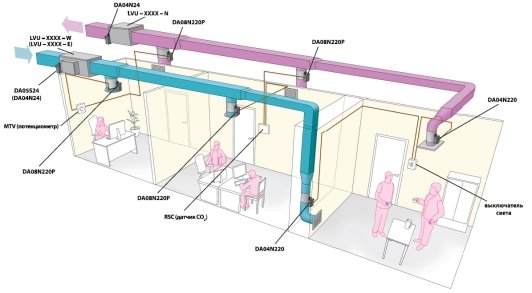
Figure 1. Outline project of the supply system to control climate in classroom [2, p. 1]
At the same time, the current trend in the development of automated ventilation climate — systems is moving in two directions [6, p. 1]:
- creation of a centralized climate — a system for the entire building or structure.
- providing individual comfortable conditions, as it is customary for passenger in aircraft and cars. In both cases, there is a climate system control panel for a separate room or passenger.
Conclusion
Thus, the adaptive system of automated control of heat and energy consumption by the institution can be optimized due to the rational use of heat and electricity. Smoothing the sharp disturbing external factors of the institution’s heat and energy supply makes it possible to smoothly and steadily regulate the consumption of these expensive resources within specified limits. Automated adaptive resource saving system has a significant impact on the financial management of an educational institution, it allows for modern scientific and technical measures for resource saving to attract additional money for an adaptive educational process and increase teachers' salaries.
References:
- Zvezdichev G.Yu. Problems and contradictions of the introduction of adaptive information systems in education // Economics and management of innovative technologies. 2016. No. 2 [Electronic resource]. URL: http://ekonomika.snauka.ru/2016/02/10673 (accessed: 02.23.2018).
- School ventilation // AeroClima.ru. URL: https://aeroclima.ru/ventilyaciya/shkoly/ (accessed: 12.04.2017).
- Models and methods for optimizing the development of energy systems. Arzamastsev D. A., Lipes A. V., Myzin A. L.-Sverdlovsk, 1976.
- Vasiliev S. N. Intelligent control of dynamic systems / S. N. Vasiliev, A. K. Zharkov, E. A. Fedosov, B. E. Fedunov. — M.: Fizmatlit, 2000.-- 352 p.
- Smirnov EM. Existing solutions to the problem of building control systems for indoor lighting // X international scientific and technical conference of students and graduate students / Abstracts. — M.: MPEI, 2004. 225–226.
- Sednin V. A. The concept of creating an automated process control system for Minsk heating networks / V. A. Sednin, A. V. Sednin, E. O. Voronov // Improving the efficiency of power equipment: Materials of a scientific and practical conference, in 2 T.V. 2. 2012.S. 481–500.

