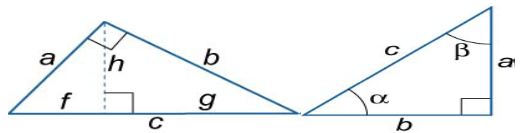
Right Triangle
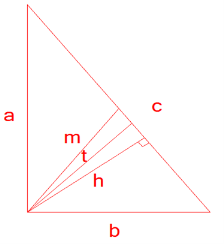
Legs of the right triangle: a,b
Hypotenuse: c
Altitude: h
Medians: ma, mb, mc
Angles: α, β
Radius of circumscribed circle: R
Radius of inscribed circle: r
Projections of the legs a and b, respectively, onto the hypotenuse c: f, g
Angle bisectors: ta, tb, tc Area: S Perimeter: L
- Determining the formula of S area for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
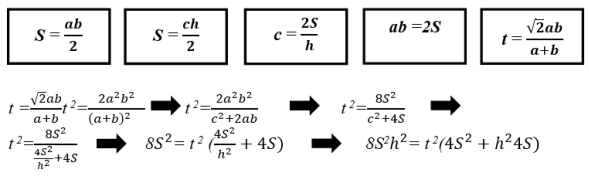
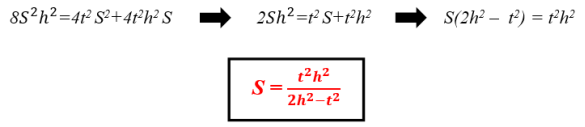
This formula is used for determining S area of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of c hypotenuse for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
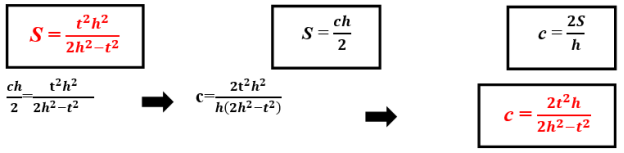
This formula is used for determining c hypotenuse of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of R radius of circumscribed circle for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.The most important formulas to find this form:
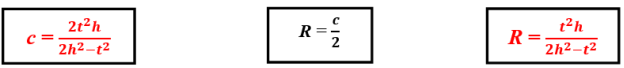
The last formula is used for determining R radius of circumscribed circle of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of a leg for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The following system is made by using Pythagorean Theorem.
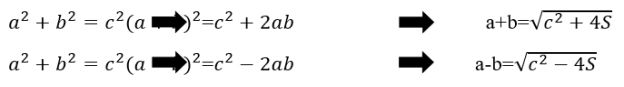
The equation is written as system appearance and then unknown parameter will be determined.
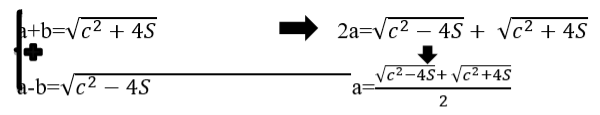
In here, the following formulas in order to determine a leg:
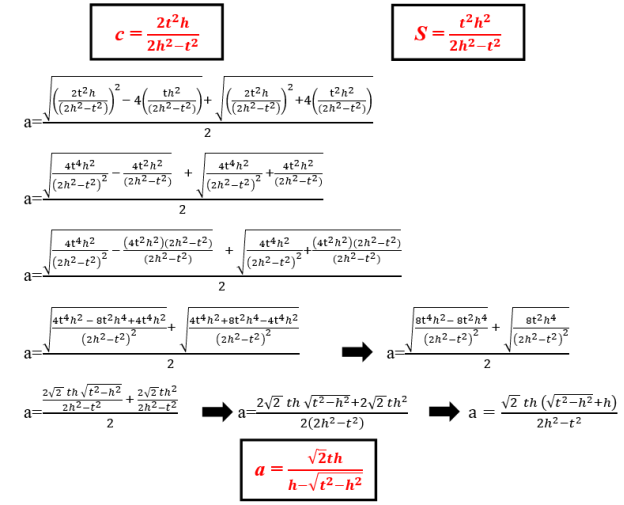
This formula is used for determining a leg of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- As the formula is known of the S area for the right triangle, b leg will be determined by using following formulas:
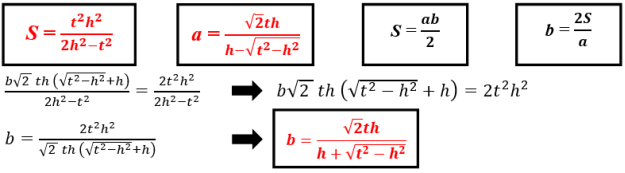
This formula is used for determining b leg of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of r radius of inscribed circle for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
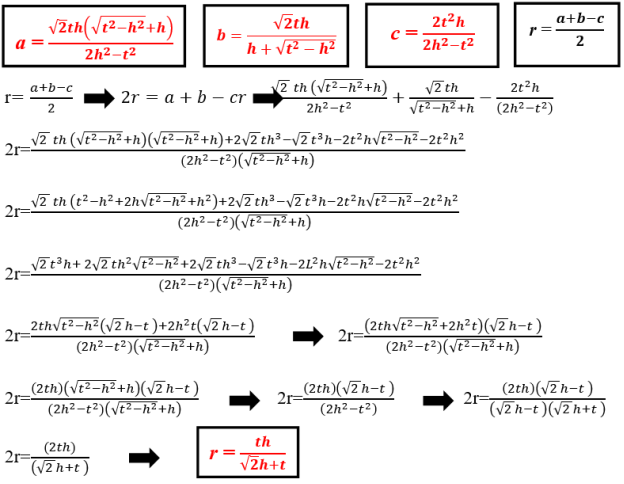
This formula is used for determining r radius of inscribed circle of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of L perimeter for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
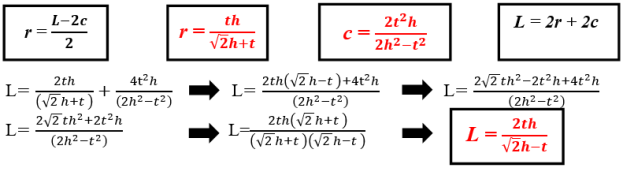
This formula is used for determining L perimeter of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of m median for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
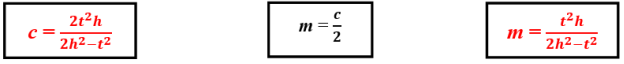
The last formula is used for determining m median of circumscribed circle of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of projection of the leg a, respectively, onto the hypotenuse c for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
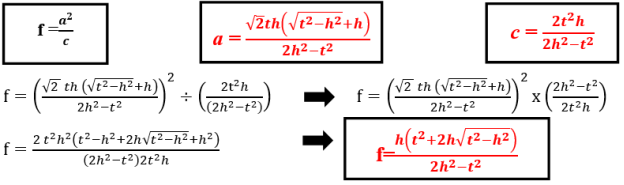
This formula is used for determining f projection of the leg a respectively, onto the hypotenuse c of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
- Determining the formula of g projection of the leg b,respectively, onto the hypotenuse c for the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle. The most important formulas to find this form:
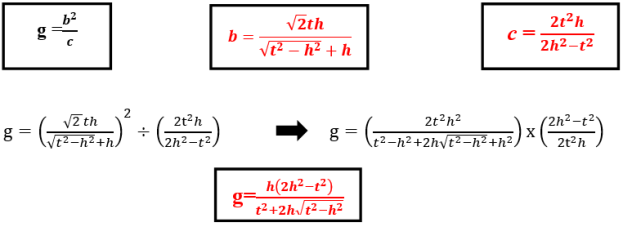
This formula is used for determining g projection of the leg b, respectively, onto the hypotenuse c of the right triangle by knowing t angle bisector and h altitude which belong to the right angle.
References:
- Alex Svirin “1300 Math Formulas” Copyright © 2004.
- A. V. Pogorelov “Analytical Geometry” Mir Publishers, Moscow, 1980.
- Israilov I. I; Pashayev Z. A. “Geometriyadan Masalalar To‘plami” Toshkent, “o‘qituvchi”, 2005.

