During the last couple of years, Russia's economy is under the burden of economic sanctions applied by the European Union and the United States as the result of the events in Ukraine. Sanctions had been applied to individuals and entities, restricting certain kinds of economic activities, including financial, technological and trade relations. The volume of trade between Russian Federation and the European Union continues to decline since 2014.
Keywords: Russia, EU, international trade, trade structure, trade flows, trading partners, sanctions
International trade is one of the oldest forms of economic relations between countries. During the historical course, it has evolved from the mere exchange of goods into present day form of trade, based on import and export of goods, services and knowledge as well.
International relations not only have economic influence, but can also be used to influence political decisions of particular countries.
Restrictive measures or «sanctions», that are the «complete or partial interruption of economic relations and of rail, sea, air, postal, telegraphic, radio, and other means of communication, and the severance of diplomatic relations» [1]. From the definition it can be seen, that the aim of using sanctions is not only to affect economic relations, but it can also lead to changes in political relations.
The mutual relations between the EU and Russia have the great impact for each of the parties. The biggest part of Russian export is realized with the European Union. The EU is also the important supplier of technologies, innovations and investments to Russia. Russia in its turn is the main supplier for natural resources as well as energy; it also provides great sources of labor. Relations based on energy supplies had established strong partners link and expanded it on investment sector.
Trade turnover of the Russian Federation with the European Union countries in 2016, according to Russian Federal Agency of Statistics, was 42,8 %. Among European partners the biggest share is with Germany — 8,7 %, the Netherlands — 6,9 % and Italy — 4,2 %.
During the period from 2004 to 2012 commodity turnover increased by more than 2,5 times and reached the highest 338,5 billion euros in 2012. However, since 2013 this indicator had negative values. So, in 2015 commodity turnover was 209,5 billion euros, that is 26,7 % reduction in comparison with 2014; of which 135,6 billion euros (-25,7 %) — Russian export and 73,9 billion euros (-28,4 %) — Russian import. But the commodity structure didn't change. In 2015, main position in goods deliveries from Russia to the EU was still taken by raw materials, such as fuel and energy goods. In import, structure dominated machines and the equipment, chemical goods and finished products.
Trade balance with EU has been negative since 2006, due to high volumes of import from Russia to EU.
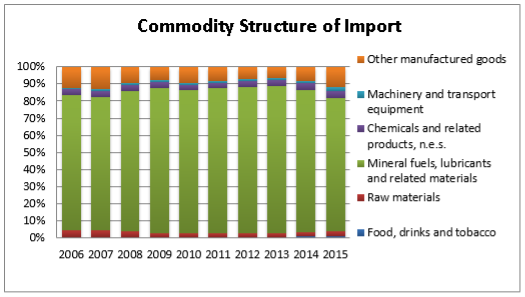
Fig. 1. Dynamics of Commodity Structure Change in EU-Russia Import
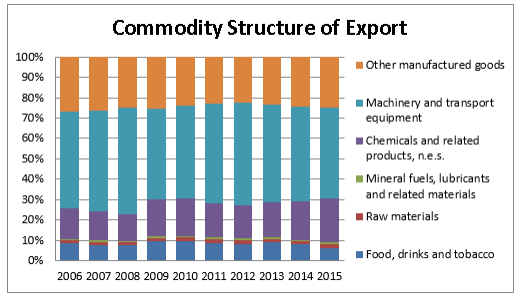
Fig. 2. Dynamics of Commodity Structure Change in EU-Russia Export
In commodity structure of the Russian import: increase in chemical products and rubber, fuel and energy goods, food products and agricultural raw materials, textiles, products from it and footwear; the share of machines, the equipment and vehicles, metals and products decreased.
Machines, the equipment and vehicles remain the main article of the Russian import in 2015. It decreased in relation to the same period of 2014 by 40,9 %, to 74,0 bln. US Dollar, at the same time the specific weight of this commodity group in structure of domestic import fell on 2,9 percent points [4]. This change is in many ways caused by devaluation of ruble, as a result of which, appeal for foreign consumer goods significantly decreased. Especially decreased import of bodies (-62,4 %) and parts (-45,9 %) of motor vehicles, other flight vehicles (-56,6 %), cars (-52,5 %) and telephone sets (-22,5 %).
Table 1
Change in EU-28 export/import with Russia
|
Jan. 2014 |
Jan. 2015 |
Jan. 2016 |
%change | |
|
Export value (euro) |
7 708 294 866 |
5 019 211 761 |
4 172 858 499 |
-46 % |
|
Import value (euro) |
17 336 974 938 |
10 331 176 609 |
8 584 557 188 |
-50 % |
|
Export quantity (kg) |
18 902 682 |
11 421 894 |
9 444 590 |
-50 % |
|
Import quantity (kg) |
372 268 782 |
323 327 210 |
346 671 181 |
-7 % |
Table 1 shows the change that happened after the sanctions were impose. In general, there is the significant decline in trade flows — 50 % decrease in import to EU and 46 % in export to Russia in euro value, since January 2014 till January 2016. Though the monetary value demonstrates almost two times drop, quantitative value shows another result: there is 50 % drop in volume of export, but import volume dropped only on 7 %. This signifies that sanctions may be not the only factor contributing to decrease in import value, because its volumes had not changed that significantly.
In service structure for the period since 2011 till 2013 there is the tendency of positive change, i.e. the increase in both trade volumes; the biggest rise is seen in import of insurance and pension services and telecommunications, computer, and information services. The biggest rise in export is in government goods, services, business services, and construction. After sanctions implementation (2014) this tendency changed into the negative one. During period of 2013–2015 the biggest drop was in importing personal, cultural, and recreational services (-57 %), maintenance and repair services (-48 %) and manufacturing services (-42 %). Export also decreased in manufacturing services on physical inputs owned by others (-56 %) and personal, cultural, and recreational services (-56 %). Financial sector, as the first one targeted by sanctions decreased by 29 % in export and 41 % in import [3].
On 6 August 2014 Russian president signed edict, prohibiting (or limiting), for a period of one year, the import of agricultural products, raw materials and food originating in countries, that have imposed sanctions against Russian entities or individuals. These counter-sanctions banned around the half of EU agrifood imports, such as fruit, vegetables, meat and dairy [2].
The Russian ban on import of the Western food has aggravated this difficult picture as it has led to increase in prices for food and as a result to inflation growth. One of the sectors that were influenced the most in trading relationships — agricultural one. Import to the EU of agricultural products decreased only by 6 %, when export to Russia decreased by 53 %.
Counter sanctions, applied by Russia on importing of agri-products, affected the value of agricultural trade between trading partners. Since these counter-measures influenced Russia itself, so the export from EU to Russia fell by 29 % since 2014 till 2015 across all sectors, i.e. total trade flow; agricultural sector fell by 39 % (picture 3), of which export of food fell by 43 %.
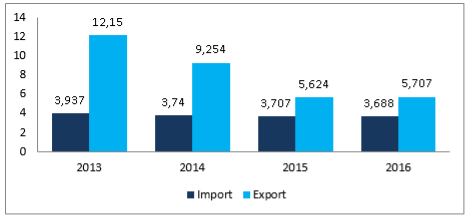
Fig. 4. EU-Russia Trade flows of agricultural products, for 2013–2016, values in Mio €
Sanctions have played a significant role in the Russian economy; another factor, that influenced it, was the fast and sharp drop in oil prices, which has begun in recent months of 2014, and it aggravated the already existing macroeconomic problems.
The latest data confirms the beginning of economic recession in Russia: GDP growth has made-2,2 % in the first quarter 2015 in comparison with the first quarter 2014 [5].
Moreover, cumulative influence of these sanctions and the drop in oil prices has led to considerable depreciation of ruble and increase in capital outflow.
At the same time, sanctions for access to financing have forced the Russian Federation to use part of currency reserves to support the enterprises and the organizations, which have fallen under sanctions [5].
After analysis of the industry structure of sanctions against Russia, it can be seen that the sanctions are directed against the key, i.e. competitive sectors of the Russian economy, such as oil and gas, as well as against the Russian banking capital.
But since the visible decline in trade volumes, that started before the year of 2014 (the year when the sanctions were applied), the sanction can be not the only reason for such decrease. Another factors contributing to this decrease can be fall of oil prices, high level of inflation or another political, military or economic reasons, but to understand that there is the need for further analysis.
References:
- Charter of the United Nations and Statute of the International Court of Justice // United Nations Treaty Collection. URL: https://treaties.un.org/doc/publication/ctc/uncharter.pdf (дата обращения: 20.03.2017).
- Economic impact on the EU of sanctions over Ukraine conflict // European Parliament. URL: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2015/569020/EPRS_BRI(2015)569020_EN.pdf (дата обращения: 20.03.2017).
- International trade statistics 2001–2017 // International trade center. URL: http://www.intracen.org/itc/market-info-tools/trade-statistics/ (дата обращения: 20.03.2017).
- Россия в международной торговле // World Trade Center Moscow. URL: http://tradestat.wtcmoscow.ru/ (дата обращения: 20.03.2017).
- Sanctions after Crimea: Have they worked? // NATO Review. URL: http://www.nato.int/docu/review/2015/Russia/sanctions-after-crimea-have-they-worked/EN/ (дата обращения: 16.06.2017).

