In modern oil and gas well construction, drilling operations are conducted under increasingly complex geological, technological, and thermodynamic conditions. The development of hydrocarbon fields is often associated with drilling through unstable formations, abnormal formation pressures, and elevated temperatures. Under such conditions, drilling fluids represent one of the most important technological elements ensuring the safety, efficiency, and economic viability of drilling operations. Drilling fluids are complex multicomponent systems that are continuously circulated in the wellbore in order to perform a wide range of mechanical, hydraulic, and physicochemical functions.
One of the primary functions of drilling fluids is the effective removal of drilled cuttings from the bottom of the well to the surface. This function is achieved through appropriate rheological properties that allow the fluid to transport solid particles upward through the annular space. At the same time, drilling fluids must be capable of suspending cuttings and weighting materials when circulation is stopped, thereby preventing sedimentation and formation of cuttings beds. Insufficient carrying capacity of drilling fluids may lead to hole cleaning problems, increased torque and drag, and stuck pipe incidents.
Another critical function of drilling fluids is the control of formation pressure. The hydrostatic pressure generated by the drilling fluid column must be sufficient to prevent formation fluids from entering the wellbore and causing kicks or blowouts. However, excessive fluid density may result in formation fracturing and loss of circulation. Therefore, careful selection and continuous control of drilling fluid density are required to maintain safe drilling conditions. Weighting materials such as barite and calcium carbonate are commonly used to regulate fluid density in accordance with formation pressure conditions.
Drilling fluids also play an essential role in maintaining wellbore stability. Interaction between drilling fluids and surrounding formations, especially clay-rich shales, may cause hydration, swelling, dispersion, and mechanical weakening of the borehole walls. These processes often result in wellbore enlargement, collapse, or stuck pipe. Properly formulated drilling fluid systems reduce fluid invasion into the formation, limit shale hydration, and help preserve borehole integrity throughout the drilling process. In addition, drilling fluids contribute to the cooling and lubrication of the drill bit and drill string, reducing friction and wear of drilling equipment.
Based on the nature of the continuous phase, drilling fluids are commonly classified into water-based, oil-based, and synthetic-based systems. Water-based drilling fluids are the most widely used due to their simplicity, relatively low cost, and environmental acceptability. These systems consist of water as the continuous phase with the addition of clays, polymers, salts, and various chemical additives to control rheological and filtration properties. Despite their advantages, conventional water-based fluids may show limited performance in reactive formations and high-temperature conditions.
Oil-based drilling fluids are systems in which hydrocarbon liquids serve as the continuous phase. These fluids are characterized by excellent lubricating properties, high thermal stability, and strong inhibition of shale hydration. Oil-based systems are particularly effective for drilling complex wells, including horizontal and extended-reach wells, where wellbore stability and torque reduction are critical. However, their application is limited by high cost, environmental concerns, and strict waste disposal regulations.
Synthetic-based drilling fluids were developed as an alternative to traditional oil-based systems in order to combine high technical performance with improved environmental characteristics. In these systems, synthetic hydrocarbons are used as the continuous phase. Synthetic-based fluids demonstrate rheological and filtration properties comparable to oil-based systems while exhibiting lower toxicity and improved biodegradability. This makes them suitable for offshore drilling and environmentally sensitive areas.
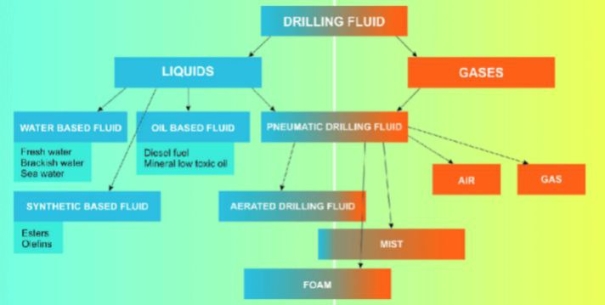
Fig. 1. Classification of drilling fluids based on the nature of the continuous phase
The performance of drilling fluids is largely determined by their rheological and filtration properties. Rheological parameters such as plastic viscosity, yield point, and gel strength influence the ability of the fluid to transport drilled cuttings, suspend solids, and ensure stable hydraulic conditions in the wellbore. Filtration properties describe the tendency of the fluid to lose its liquid phase into permeable formations. Excessive filtration may result in formation damage, differential sticking, and reduction of well productivity. Therefore, drilling fluids are formulated with filtration control additives to form thin, low-permeability filter cakes on the borehole wall.
Environmental considerations play an increasingly important role in drilling fluid selection. Modern drilling operations require the use of low-toxicity additives and environmentally acceptable fluid systems. This has stimulated the development of biodegradable polymers, environmentally friendly lubricants, and synthetic-based drilling fluids with reduced environmental impact.
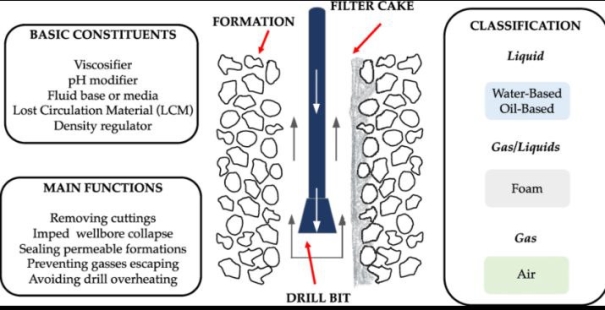
Fig. 2. Main technological functions of drilling fluids in the wellbore
Analysis of drilling practice indicates that there is no universal drilling fluid system suitable for all geological and technological conditions. The selection of an appropriate drilling fluid must be based on a comprehensive assessment of formation properties, drilling objectives, environmental requirements, and economic constraints. Proper control of drilling fluid properties is essential for ensuring wellbore stability, safe drilling operations, and overall drilling efficiency.
References:
- Caenn R., Darley H. C. H., Gray G. R. Composition and Properties of Drilling and Completion Fluids. Houston: Gulf Professional Publishing, 2017.
- Bourgoyne A. T., Millheim K. K., Chenevert M. E., Young F. S. Applied Drilling Engineering. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1986.
- Amanullah M., Al-Arfaj M. K. Drilling fluid rheology and hydraulics. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2011, Vol. 77, pp. 334–343.
- Ismail A. R., Rashid N. M. Environmental impact of drilling fluids. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2013, Vol. 57, pp. 1–10.

