To overcome and minimize the number of pesticides, this study presents safe biological nano-emulsions from silver nanoparticles, neem oil, and polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) with nanoparticle sizes ranging from 42 to 78 nm, inhibiting Fusarium oxysporumfungi at a concentration of 5 ppm on a silver basis in an in vitro laboratory. Nano-emulsion applied in organic agricultural production is a new direction to initially help reduce the use of chemicals towards green agricultural production.
Keyword: Azadirachta indica, Chrysanthemums, Nano-emulsion, Silver, Polyhexamethylene biguanide.
1. INTRODUCTION
The ornamental flowering plant Chrysanthemum indicum L. ( C. indicum L.), primarily derived from Chrysanthemum indicum L. a member of the Compositae family, is a perennial plant that has been used as a traditional medicine for more than 2000 years in China and is widely used for the treatment of Pemphigus, swelling, pain, and scrofula [1]. Chrysanthemum holds substantial significance in the realm of ornamental plants, ranking closely after roses, and is of considerable commercial value in the cut-flower industry. However, cultivated commercial varieties are vulnerable to various biotic and abiotic stresses, which can compromise their ornamental quality and market value. A wide array of phytopathogens, including fungi, bacteria, viruses, viroids, and phytoplasmas, significantly impact chrysanthemum cut-flower production. Among these, Fusarium wilt has become increasingly prevalent as a fungal disease in recent years [2]. This soil-borne pathogen can persist in both soils and plants throughout the plant growth cycle, acting as a source of inoculum for subsequent seasons. For instance, Fusarium wilt in chrysanthemum (F. oxysporum ) is known to initiate symptoms by invading the roots, subsequently obstructing vascular bundles, disrupting nutrient uptake, and ultimately resulting in symptoms like yellowing, wilting, and eventual plant death. This soil-borne pathogen can persist in both soils and plants throughout the plant growth cycle, acting as a source of inoculum for subsequent seasons. For instance, Fusarium wilt in chrysanthemum (F. oxysporum ) is known to initiate symptoms by invading the roots, subsequently obstructing vascular bundles, disrupting nutrient uptake, and ultimately resulting in symptoms like yellowing, wilting, and eventual plant death [3]. The current approach to fungal disease management involves the direct application of chemical pesticides to plants to restrict disease progression and mitigate its impact on crop yields. However, the indiscriminate use of chemical pesticides adversely affects the health of cultivators, the ecological environment, and consumers. To replace chemical pesticides, biologically active alternatives need to be researched, developed, and implemented.
Nanotechnology in crop disease management and prevention is being investigated and progressively refined by domestic and international scientists [4]. Elements such as zinc, copper, and silver exhibit potent antifungal and antibacterial properties. When metallic nanoparticles are reduced to nanoscale dimensions, their antibacterial and antifungal efficacy increases a thousandfold compared to their ionic counterparts. Moreover, their toxicity demonstrates high selectivity towards bacteria and fungi. Studies by various authors [5] have shown that silver nanoparticles possess strong antagonistic capabilities against numerous pathogenic fungi, including Puccinia spp., which causes rust disease in chrysanthemums, and Plasmodiophora brassicae, responsible for clubroot disease in cabbage. Low-concentration silver nanoparticle applications have shown effectiveness against brown spot disease ( Alternaria passiflorae ) and yellowing disease ( Fusarium sp.; Phytophothora sp.). Recent research findings indicate that the combined use of silver and copper nanoparticles produces a synergistic inhibitory effect, effectively preventing various fungal pathogens [6]. Certain insect control products (pheromones, methyl eugenol) manufactured as nano-gels have proven effective, showing great potential and high biological safety for crops. However, the use of metallic nanoparticles remains limited due to their poor adhesion or instability in intense light environments.
Currently, nano-emulsion formulations offer numerous advantages over traditional concentrated emulsions, including reduced phytotoxicity due to decreased organic solvent usage, controlled release of active ingredients, enhanced biological activity, minimized environmental pollution, and improved user safety [7]. Antibacterial nano-emulsions (NEs) are oil-in-water droplets with diameters ranging from 200 to 600 nanometers. NEs are effective against bacteria ( E. coli, Salmonella, S. aureus ), enveloped viruses (HIV, Herpes simplex ), fungi ( candida, dermatophytes ), and spores. The emulsion phase inversion (EPI) method is a low-energy approach to nano-emulsion formation based on phase inversion at a fixed temperature, typically room temperature [8]. This phase inversion is achieved by altering the ratio of oil and water components in the emulsion system.
Neem oil is an essential oil extracted from different parts of the neem tree ( Azadirachta indica ), a native tree from the drier regions of Asia and Africa that is considered a very important medicinal plant. So far, more than 300 phytochemicals, chemically diverse and structurally complex, have been extracted and isolated from different parts of this tree: from leaves-azadirachtin, nimonol, nimocinol and nimocinolide; from barks-gallic acid, gallocatechin and epicatechin; from seeds-azadirachtin, azadiradione, nimbin, salannin and epoxyazadiradione. These chemical compounds have demonstrated a wide range of unusual effects against a wide spectrum of pests (insects, fungi, and viruses) [9]. Silver nanoparticles synthesized using Azadirachta indica extract, with particle sizes ranging from 10 to 60 nm, have demonstrated high efficacy in eliminating bacteria and fungi [10,11].
The antibacterial properties of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) are attributed to interactions between the bacterial cell membrane's lipid bilayer and guanidine groups, resulting in the loss of lipid bilayer fluidity or dissolution, inhibition of cell growth, and ultimately bacterial cell death [12]. As a positively charged, high-molecular-weight organic polymer salt, PHMB exists in liquid form (oil emulsion) with Polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride as its primary component. PHMB can diffuse through cell membranes, forming complexes with phospholipids, destabilizing osmotic equilibrium, and disrupting cell membranes [13]. Due to its high water solubility, excellent bactericidal efficacy, low toxicity, odorless nature, non-corrosiveness, and high stability, PHMB can be utilized as a disinfectant, particularly in the production of antibacterial fabrics, medical materials, and water treatment. Numerous studies have formulated silver nanoparticles in PHMB and evaluated the formulation's ability to inhibit Staphylococcus aureus growth. Experimental results indicate that the silver nanoparticle — PHMB formulation exhibits significantly superior bactericidal capabilities compared to the silver nanoparticle and PHMB solutions independently [14].
Organic agricultural production aims to employ biologically safe plant protection products in plant disease control. Research into using biological nano-emulsion formulations derived from silver, neem oil and PHMB for controlling various diseases in chrysanthemum plants represents a novel direction that requires focused research and development efforts.
- MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Materials
Nanoemulsions from silver and Neem oil, PHMB are synthesized at the Institute of Science and Technology for Energy and Environment — Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology. The fungus strain that causes Fusarium wilt disease is provided by the Institute of Biotechnology — Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology. PDA culture medium (Merck).
2.2. Methods
Nano-emusion: Preparation of nanoemulsion from nano silver, PHMB, and neem oil: (I) — Using AgNO 3 precursor salt dissolved in RO water according to Ag + content of 1.5g/L. (II) — Adding quaternary ammonium cationic surfactant PHMB with a content of 30g/L stirred vigorously (1500 rpm). (III) — Neem oil with the active ingredient Azadirachtin is added slowly to (II) and stirred continuously, the stirring reaction takes place for 20 minutes. The resulting mixture is incubated in a dark chamber for 24 hours at room temperature to prevent the self-oxidation of silver nitrate. The formed Nanoemulsion was evaluated by the spectral method on Hitachi UH-5300 UV-Vis; the Transmission electron microscopy method was measured on HR-TEM sewing at the Institute of Materials Science — Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology; The nanoparticle size distribution and zeta potential of the sample were measured on the SZ-100 machine at the Institute of Science and Technology for Energy and Environmental after the timelines after 0 days, 30 days, 60 days and after 90 days of storage.
Antifungal activity: Nanoemulsions were evaluated for antifungal resistance under in-vitro laboratory conditions and inhibitory dose selection. For fungal diseases, the method of determining the diameter of the fungus is used [15]. The concentration selection experiment in the Invitro laboratory used 5 formulations of 1ppm, 3ppm, 5ppm, 7ppm, and 10ppm in silver. Repeat each experiment 3 times to get the average data. The inhibitory effect is determined according to the Abort formula as follows:
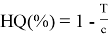
HQ: Efficacy of in vitro
T: Diameter of fungus experimental formula
C: Diameter of fungus control
- RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Synthesis of nanoemulsion plant protection products
The formation of emulsions containing silver nanoparticles is visually assessed by the color change. The addition of Azadirachta indica (Neem) extract to AgNO 3 solution results in a change in the color of the mixture from yellowish to reddish-brown, indicating the formation of Ag-NP (Figure 1). Surface Plasmon resonance of nanoparticles in the reaction mixture. This was also reported by several other studies that observed a change in color in the reaction mix during the formation of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from the species Oscillatoria, Allium sativum, Zingiber officinale, and Capsicum frutescens [16]. The results obtained from the UV-Vis spectrum show the appearance of silver nanoparticles that have been formed. In the study, the Plasmon peak of biosynthetic Ag was observed at a wavelength of 412 nm just like other studies in the world. The adsorption peak is sharp and has a high adsorption intensity. This result shows that Nanosilver is relatively small and fairly uniform in size.
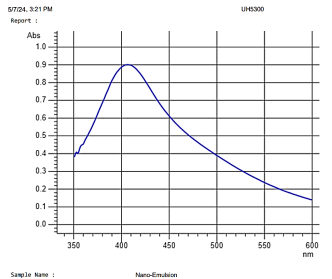
Fig 1. Maximum wavelength image of nano-emulsion containing silver nanoparticle
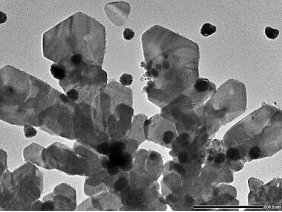
Fig 2. Image TEM of nano-emulsion containing silver nanoparticle
In Figure 2, the image TEM of the nanoemulsion preparation shows that silver nanoparticles are formed with a size of 50nm. Small particle size can increase over time through the Ostwald reaction — this physical instability causes self-assembly into larger particles.
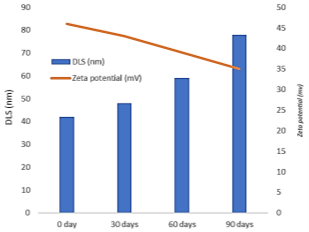
Fig 3. Dynamic Light Scattering — DLS and zeta potential of nano-emulsion
Nanoparticle size distribution and zeta potential of the emulsion preparation were examined immediately after synthesis and after storage periods of 30, 60, and 90 days in Figure 3. A gradual increase in the particle size distribution of composition from 42nm up to 78nm after 90 days, shows the phenomenon that nanoparticles tend to self-assemble. This is also proven by the measured zeta potential, which decreased significantly from 46 mV to 35 mV, showing that the stability of the product has decreased but is still quite stable.
3.2. Antifungal activity of nano-emulsion
Mix the nano-emulsion product after preparation with a determined concentration into the PDA agar medium, and evaluate the ability to inhibit fungal pathogens by comparing it with the control PDA medium (not containing the nano-emulsions) after 7 days.
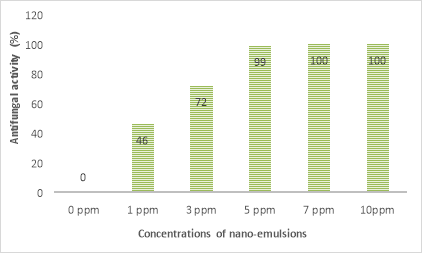
Fig 4. Antifungal activity Fusarium oxysporum of nano-emulsion in vitro
Experimental results shown in Figure 4 show that all nanoemulsion samples at concentrations from 1 to 10 ppm showed inhibition against the fungus Fusarium oxysporum . At the lowest concentration (1 ppm), the product sample was able to inhibition fungi by 46 % after 7 days. When increasing the concentration of the product from 5 ppm, the ability to inhibit fungi reached approximately 100 % as observed that fungal spores hardly developed after the 3rd day on agar medium.
- CONCLUSION
Nano-emulsion applied in organic agricultural production is a new direction when it can combine extracted biological active ingredients with metals with high antiseptic properties such as silver and increase the effectiveness of disease prevention. The Nano-sized emulsion product created after 3 months of storage remains stable at 78 nm and is effective at 5 ppm based on silver, inhibiting 100 % of the fungus that causes Fusarium oxysporum wilt disease in the laboratory.
Acknowledgement: The project is supported by project code CSTRE 01/24–25 of the Institute of Science and Technology for Energy and Environment.
References:
- Shao Y. Et al. Chrysanthemum indicum L.: A Comprehensive Review of its Botany, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology // Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020. Vol. 48, № 04. P. 871–897.
- Balamurugan A. et al. Chrysanthemum wilt caused by Fusarium incarnatum: Etiology unveiled through polyphasic taxonomic methods // Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024. Vol. 129. P. 102214.
- Miao W. Et al. Potential pathways and genes expressed in Chrysanthemum in response to early fusarium oxysporum infection // BMC Plant Biol. 2023. Vol. 23, № 1. P. 312.
- Shaimaa H. Abd-Elrahman and M. A. M. Mostafa. Applications of nanotechnology in agriculture: An overview Egypt”, J. Soil Sci. 2015. 55(2), pp.1–19.
- Singh S. Et al. Applications of Nanotechnology in Agriculture and their Role in Disease Management // Res. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015. Vol. 5, № 1. P. 1–5.
- Djiwanti S. R., Kaushik S. Nanopesticide: Future Application of Nanomaterials in Plant Protection // Plant Nanobionics / ed. Prasad R. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019. P. 255–298.
- Nagar M. Review on Nano-Emulsion Drug Delivery System and Formulation, Evaluation and Their Pharmaceutical Applications // Int. J. Health Care Nurs. 2023. Vol. 2, № 1. P. 35–61.
- Hien L. T. M., Khoa T. D., Dao D. T. A. Characterization of black pepper essential oil nanoemulsion fabricated by emulsion phase inversion method // J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022. Vol. 46, № 1.
- Rodrigues M. P. et al. In Vitro Activity of Neem (Azadirachta indica) Oil on Growth and Ochratoxin a Production by Aspergillus carbonarius Isolates // Toxins. 2019. Vol. 11, № 10. P. 579.
- Kumari S. A., Patlolla A. K., Madhusudhanachary P. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Azadirachta indica and Their Antioxidant and Anticancer Effects in Cell Lines // Micromachines. 2022. Vol. 13, № 9. P. 1416.
- Ahmed S. Et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract // J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016. Vol. 9, № 1. P. 1–7.
- Ashraf S. et al. Polyhexamethylene biguanide functionalized cationic silver nanoparticles for enhanced antimicrobial activity // Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012. Vol. 7, № 1. P. 267.
- Siadat S. A., Mokhtari J. The Role of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide and Silver Nanoparticle Interaction in the Fabrication of Novel Antibacterial Bio-Fibers Using Silk Wastage // J. Nano Res. 2016. Vol. 43. P. 63–72.
- Yi J. Et al. Effect of polyhexamethylene biguanide functionalized silver nanoparticles on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus // FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019. Vol. 366, № 4.
- Ouda S. M. Antifungal Activity of Silver and Copper Nanoparticles on Two Plant Pathogens, Alternaria alternata and Botrytis cinerea // Res. J. Microbiol. 2014. Vol. 9, № 1. P. 34–42.
- Otunola G. Et al. Characterization, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized from aqueous extracts of Allium sativum, Zingiber officinale, and Capsicum frutescens // Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017. Vol. 13, № 50. P. 201.

