Face recognition technology in a variety of biological technology recognition, it has the characteristics of operation hidden non-contact collection concurrency tracking ability after strong simple operation, in many places can be widely used in this paper in the infrared face recognition algorithm on the basis of KJ-Face Face recognition algorithm and LFA Face recognition algorithm.
Keywords: face recognition, biological characteristics, face capture, biometric authentication technology, feature extraction
Introduction
Automatic identity recognition technology is a new force; most automatic identification systems use biometric recognition technology. Biometric identification technology is now the authentication technology research, points, biometric identification technology study some strong stability and difference in different between different individual intrinsic attributes, and facial recognition technology is a research branch in biological recognition technology, further extract individual identity features, these features and the face database model [1].
Overview of Face Recognition Algorithm
With the development of science and technology, human society is growing, at the same time, various means of criminals is becoming more and more high-end, camouflage ability more and more hidden, the existing monitoring and security system to produce new challenges, face recognition algorithm is a new research subject, this paper face recognition system is mainly based on the following three kinds of face recognition technology [2]:
Infrared face recognition technology
Infrared face recognition technology uses infrared technology, greatly improve the ability to adapt to the change of light intensity, suitable for indoor and outdoor, day and night, there are lights and lights of all types of places. In addition to infrared technology with high recognition rate, color camera is also used to capture face image registration for later inquiry. Infrared face recognition advantages of small contact, intuitive, good accessibility, etc. The method of infrared face recognition is shown in Figure 1.

Fig. 1. Infrared face recognition
KJ-FACE Face recognition technology algorithm
Dynamic Local Feature Analysis (DLFA) is a novel and efficient face recognition technology. As shown in figure 2, the first to face image preprocessing, the purpose is to remove photos too much noise, people will lose face images with edge adaptive detection method is converted to binary images, and then extracts the facial skin texture (namely the dermatoglyph, as shown in figure 2 on the right), and then use the local feature analysis method to deal with the edge of the shadow of the face and skin, so as to recognize faces.
![]5SKPTB~A[NL_9_49JKSFHH](https://articles-static-cdn.moluch.org/articles/j/93152/images/93152.002.png)
Fig. 2. KJ-Face Face recognition
Local feature analysis algorithm
Local Feature Analysis, LFA algorithm uses a Local Feature representation similar to the statistical principle of building blocks, based on the principle that all faces can be synthesized by many structural units and sub-blocks that can no longer be simplified. LFA use 32 to 50 child area to identify a human face, choose commonly used frequency points such as the face of the nose, eyes, mouth and specific bone cool curvature difference as a block element, sub-block is the use of statistical techniques to form complex, they represent the entire face, often across multiple pixels and represents the common face shape, but not usually in the sense of facial features, to be sure A face is determined not only by its feature blocks, but also by its geometric structure (such as shape and relative position).
System Functions overview
Face capture
Face recognition system to be able to pass the camera face detection and face pedestrians are extracted, and storage management, and then according to the system Settings of the camera is then used contrast mode (blacklist model / white list) will capture the qualified face image is sent to the background face compared to server, to obtain recognition as a result, to achieve the set similarity threshold is to produce a report to the police. After the event, the operator can refer to the alarm record or face recording process picture and transfer it to the video at that time for video playback [3]. The face capturing case is shown in Figure 3.
![`5(2Y5W(])9UE01Z5ZDV57U](https://articles-static-cdn.moluch.org/articles/j/93152/images/93152.003.png)
Fig. 3. Flow chart of face comparison recognition
Face recognition and alarm
Face recognition system can be deployed on the face of the channel, each channel can be configured separately blacklist database, to achieve a separate deployment. Face comparison recognition mainly uses face recognition algorithm to capture the face image modeling, at the same time with the blacklist database of the face model in real time comparison, if the face acquaintance reaches the set threshold, the system can automatically through sound and other ways of warning, remind the monitoring management personnel. The monitoring manager can double-click the alarm information to check the original picture and video for verification. The specific process is shown in Figure 4.
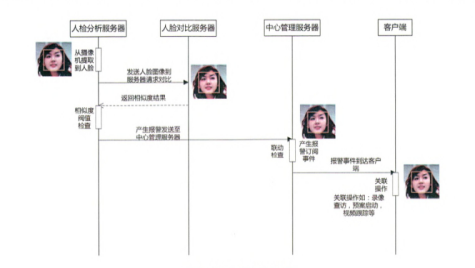
Fig. 4. Flow chart of face comparison recognition
Limitations of Face Recognition System
The face recognition rate is still limited by many conditions. A detailed understanding of the limitations of the face capture comparison system is a key link in the application of the system. The following eight face capture techniques and recognition avoidance are all good practices summarized in practice [4]:
— Similarity;
— Variability;
— Quality;
— Face photo angle;
— Shielding interference;
— The influence of light;
— Blacklist source;
— Blacklist database size.
References:
- M. Wang and W. Deng, “Deep face recognition: A survey,” NC, vol. 429, pp. 215–244, Mar. 2021.
- M. J. Paul Viola, «Robust Real-time Object Detection», International Journal of Computer Vision, pp. 137–154, 2004.
- A. Bansal, K.Mehta, S. Arora “Face Recognition using PCA Algorithm and LDA” IEEE Second International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Technologies, pp 251–254, 2012.
- J. Zhou, G. Su, C. Jiang, Y. Deng, and C. Li, «A face and fingerprint identity authentication system based on multi-route detection», Neurocomputing, Vol.70, pp.922–931, 2007.

