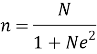The widespread overuse of pesticides in agriculture has raised concerns about their negative impacts on human health and the environment. The knowledge and awareness of farmers are important factors for safe and effective use of pesticide. Research shows limited knowledge and awareness of farmers in the district of Phu Ninh about negative impacts on health and the environment, as well as how to safely use and handle residual pesticides and used containers/packages. Most of the farmers participating in the survey were quite old (100 % over 40 years old) and had low levels of education, which may contribute to the situation. Based on the results of the survey, the study also proposed groups of solutions for three main stakeholders participating in the safe and efficient management and use of pesticides: local managers, business households trading, distributing pesticides and farmers directly buying and using pesticides.
Key words: pesticide, awareness of farmers, pesticide management, pesticide practice
1. Introduction
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), every year, damage from diseases and pests have caused an average of a 20–30 % loss in the total annual product. The use of pesticides has become one of the most effective methods in the field of eliminating harmful threats and preserving agriculture, and maintaining product security. The field of pesticides is becoming increasingly important for the development of Vietnam’s farming industry.
With natural and diverse environmental conditions, Vietnam is a country with a considerable cultivatural advantage, and has developed a large plant industry to meet national and worldwide demands for exporting. However, due to our country’s hot and humid weather, diseases and pests are a year-round problem, causing damage to harvest and in turn impacting the quality and quantity of produce. Because of that, using pesticides to eliminate potential harms to crops is still an important and widely used solution. However, the situation shows that the people’s limited knowledge of pesticides leads to ineffective usage and also causes a lack of product safety and heavy pollution. According to international experts, 80 % of pesticides are used incorrectly and inefficiently (Le Tam, 2016). Especially in poor agricultural regions, people use pesticides that are cheaper, but are outdated and more poisonous.
Phu Ninh is a plains district in the dynamic economy zone of the Quang Nam province, the area of transition between the plains and the midlands. On the basis of natural conditions, the advantage of the area, along with the Phu Ninh lake, aims to serve the purpose for the irrigation of agriculture. Every year, the district has had an area of up to over 32.000 ha for cultivating wheat, 1.400 ha for growing cassava, 500 ha for sweet potato, 800 ha for pumpkin, and along with other different crops. The area also has tropical humid weather, with an average temperature of 25℃ and a high amount of rainfall averaging at about 2600mL per year. These conditions make for a very convenient development in the agricultural field but also give the appropriate conditions for the progression of harmful insects and diseases. Because of this, using pesticides is an important and needed action. Pesticides are used in different development stages of plants leading to a steady increase in usage and making them more common in the district. Besides from the benefits of eliminating pests and diseases when used correctly, improper use of these chemicals can lead to many severe consequences, for example if used with inaccurate techniques, not following warnings or guidelines, or misusing it, killing helpful insects, and excess chemicals or their packaging can cause pollution to dirt and groundwater, having a negative effect on human and environmental health. Because of these risks, properly assessing the use of pesticides and applying measures to reduce their environmental and medical impact in the district of Phu Ninh in the Quang Nam province is necessary and urgent.
Because of the above mentioned reality, a research on the topic of “The state of pesticide use in the Phu Ninh district of Quang Nam province and suggesting solutions for safer and more controlled use” was carried out.
2. Research methods
2.1. Secondary data collection method
Collecting data on natural conditions and the situation of society and economics of the Phu Ninh district of Quang Nam province through past investigations and information from trustworthy departments.
2.2. Method of surveying through questionaires and interviews
Surveys with people in the agricultural field in the local area. Idenify the samples using the Slovin formula (Yamane, 1973) shown with the formula (1) .
The Slovin formula:
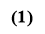
|
|
In which:
n: Sample size (amount of representative households in the angricultural manufacturing industry); N: Total amount of agricultural households in the local area of investigation; e: Margin of error (usually set to be 0.05)
The total amount of agricultural households in Phu Ninh is about N=17.987 (households) (Source: Phu Ninh district Statistical Office, 2020). Calculating with the formula (1) , the sample size was 99 (households), Corresponding to 99 questionaires for the agrucutural manufacturing individuals in the local area of the Phu Ninh district, Quang Nam Province. The questionaires of the survey were distributed with a random method. The investigation method uses surveys combined with observation and interviewing about the investigation subjects like farmers and managers.
Table 1
General information of respondents to the questionaire
|
Information |
Amount of households |
Ratio (%) | |
|
Gender |
Male |
56 |
57 % |
|
Female |
43 |
43 % | |
|
Age group (Age) |
40–45 |
31 |
31 % |
|
45–50 |
53 |
54 % | |
|
>50 |
15 |
15 % | |
|
Education level |
Not schooled |
8 |
8 % |
|
Primary school |
36 |
37 % | |
|
Middle school |
29 |
29 % | |
|
High school |
15 |
15 % | |
|
Undergraduate or higher |
11 |
11 % | |
|
Occupation |
Agricultural sector |
99 |
100 % |
2.3. Method of data analysis
Using the Excel software to process and present the collected data.
3. Research results and discussion
3.1. Natural conditions, economical and social characteristsics
3.1.1. Natural conditions
3.1.1.1. Geographical location
Phu Ninh is a district separated from Tam Ky city, Phu Ninh is 30km North of from Chu Lai airport, Ky Ha port, and 70km South of Da Nang city. With a main border as follows:
It’s East border is adjacent to Tam Ky with a length of over 21 km and the Nui Thanh district with a length of over 30 km; The West border is adjacent to the Tien Phuoc district with a length of 32.8 km; On the South, the border is adjacent to the Bac Tra My district with a length of 9 km; The North border is adjacent to the Thang Binh district with a length of 19,4 km.
Fig. 1. Geographical map of Phu Ninh district (Google maps, 2022)
3.1.1.2. Terrain
Mostly comprised of alternating low mountains and hills, with decreasing height levels from West to East.
Total land area is 25,565 ha, of which: Agricultural land: 11,760 ha; Forestry land: 7,626 ha; Specialized land: 4,349 ha; Residential land: 676 ha (Department of Planning and Investment of Phu Ninh district, 2020).
3.1.1.3. Climate
Phu Ninh is situated in a humid tropical area, with seasonal winds of the Dong Truong Son area divided into 2 separate seasons, the rainy season and the dry season. The average temperature is 25 0 C, and the average rainfall is 2.600 mm. The average yearly air humidity is 83–86 % (Planning and Investment Department of Phu Ninh, 2016).
3.1.1.4. Hydrological dynamics
The Phu Ninh lake is the largest irrigation lake in the whole province, with a volume of over 370 m 3 . It helps with climate control and providing fresh water for agriculture and daily life for the entire area. Outside of the Phu Ninh lake, the area also has small rivers and creeks like: Ban Thach river, Bong Mieu river, La Ga creek, Nha Ngu creek, Tay Yen creek, Truong Chi creek, with unsubstantial water flow.
3.1.2. Economical and social development
Administrative organization: The Phu Ninh district has 11 commune administrative units (10 communes, 01 town). The population of Phu Ninh district is 80344 people. The economic structure of the district: Agriculture — Construction Industry — Trade and Service is 22 % — 44.5 % — 33.5 %, respectively. In which, the agricultural value contributes to about 932 billion VND per year.
3.2. Situation of trading and distribution of pesticides of business establishments
Through investigations of the situation of the use of pesticides in the district of Phu Ninh, results show that pesticide-selling agencies have the following common traits:
— A large percentage of local pesticide sellers are of small branches. The display location of the pesticides if also a day-to-day living space, but the stockpile is located elsewhere. The main customers are the local people. In general, the products are for sale according to the ordinance on pesticides in Vietnam.
— All store owners were educated on pesticides and were provided with certificates before opening their business. The facilities said that the most popular drugs today are growth and prevention and control of pests and diseases. The best-selling drugs are chemical plant protection drugs.
— February and March are the months when the highest amount of pesticides are sold because this is the winter-spring harvest of farmers. The lowest amount of pestcides sold is on around November and December because at this time, the sowing season has not yet started. In general, agents strictly comply with the allowed list of products according to the regulations of the government.
3.3. Pesticide usage of farmers in Phu Ninh town
According to the survey results of 99 households in Phu Ninh district, more than 95 % of households had pest problems in agricultural production and more than 98 % of households applied pest control measures.
3.3.1. Types and dosages of pesticides
Through surveys and interviews with farmers, it is found that the types of pesticides being used in Phu Ninh are diverse, including insecticides, herbicides, growth-stimulated drugs, etc. However, most of the people do not remember clearly or incorrectly remember the name of the pesticides they used.
When seeing the appearance of pests and diseases, farmers often go to drug stores to buy pesticides, talk about the symptoms of the disease, and then buy chemical pesticides to spray. The business owner will guide how to mix the chemicals as well as the selection of pesticides for people.
The diversity of types and function of pesticides helps people to easily and conveniently approach, but it also causes many difficulties in quality control of pesticides in the district.
Through interviews at pesticide trading businesses, the most commonly used drugs were found, as well as the spray quantity and unit price shown in Table 2. The list of frequently used pesticides and their prices market as of November 1, 2021.
Table 2
List of frequently used pesticides and market prices as of November 1, 2021
|
No |
Name of pesticide |
Agricultural subject |
Objects of prevention and treatment |
Spray amount |
Price (VND) |
|
1 |
AGR0NIL 75WP |
Rice, Watermelon |
Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn Downy mildew |
400L/ha |
7000/ package |
|
2 |
VICTORY 585EC |
Rice |
Brown planthoppers Stem borers |
24mL/ 16–20L water |
25000/ bottle |
|
3 |
KASUMIN |
Rice Vegetables Cabbage Peanut Orange |
Mint rust (Puccinia menthal pers.) Magnaporthe grisea (Pyricularia oryzae) Bacterial rot (Erwinia carotovora) Leaf spot Colletotrichum gloeopsoriodes |
32–35mL/ 16L water |
6000/ package |
|
4 |
DAIWANTIN 5.0EC |
Rice Peanut |
Pesticide-resistant caterpillars |
4–6mL/ bottle of 8L |
32000/ bottle |
|
5 |
NERTOX 95WP |
Rice |
Stem borers Cnaphaclocrocia medinalis Paddy thrips (Thrips oryzae) |
20g/16–20L water |
7000/ package |
|
6 |
DANOBULL 50wp |
Rice |
Mealybugs Leafroller caterpillers Stem borers |
400–600L/ ha |
7000/ package |
|
7 |
ANVIL 5SC |
Rice Corn |
Pricly pear Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn Leaf spot on peanut |
320–600mL/ ha |
12000/ package |
3.3.2. Choices of types and how to use pesticides of farmers
The results of the interviews with 99 households in Phu Ninh district about the selection and use of pesticides are shown in Figure 2.
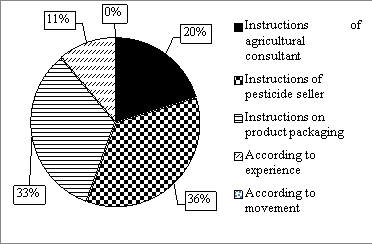
Fig. 2. Respones of farmers on how they used pesticides
Responses from interviewed farmers on how they used the pesticides presented in Figure 2 shows that a relatively large percentage used pesticides according to the instructions of the sellers (36 %), following the instructions on the production packaging accounted for 33 %, usage under the guidance of agricultutral officials was not high 20 %. This result about farmers' high dependence on information and knowledge is in agreement with Jallow et al. (2017). In addition, according to the survey, 95 % of households did not attend training before using pesticides, only a few households participated in training. Participating in training programs helps increase understanding of safety precautions while handling pesticides (Chen et al. 1998; Jones et al. 2009). The source of information and the extent to which farmers trust informants can shape their perception of pesticide risks and the adoption of preventive measures (Rios-Gonzalez et al. 2013). This is an important fundamental for providing solutions towards improving farmers' knowledge and awareness about pesticides and safety for the environment and human.
3.3.3. Results on the time of pesticide spraying
The chart of the time of spraying pesticides by interviewing 99 households is shown in Figure 3.
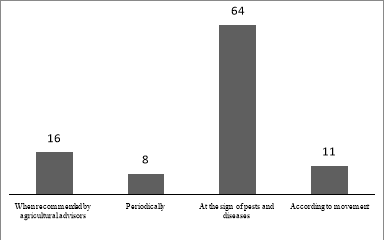
Fig. 3. Time of pesticide spraying
Figure 2 shows that 64 % of households choose to spray when seeing signs of pests and diseases; 8 % of households spray periodically, this indicates that prevention is better than cure, but this can potentially pollute the environment and cause waste of chemicals as well as money. Only a small percentage of farmers sprayed when recommended by the agricultural advisors (16 %). Spraying according to the movement accounted for a small proportion of 11 % in the whole district, but partly reflected the lack of knowledge and awareness on the issue of effective and safe use of pesticides.
3.3.4. Ways the farmers handle residual pesticides after spraying
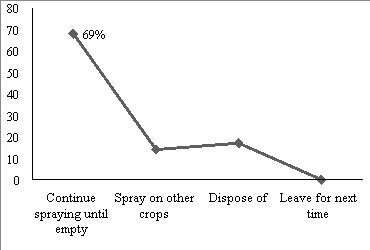
Fig. 4. Ways the farmers handle residual pesticides after spraying
Surveyed households would use all the pesticides for the same crops, accounting for a very high rate 69 %. Some households said that the process of using pesticides sometimes has excess medicine, usually households will spray on areas with more severe pests than the rest until nothing left. There are also some other cases, for example pesticides could be used for other crops but the rate was not high at 14 %. 17 out of 99 households disposed excess pesticides, which was accounting for 17 %. These poor pesticide handling practices can lead to harmful residues in catches, soil and water pollution, posing a threat to both human health and the environment [Atraya et al. 2012].
3.3.5. Ways the farmers handle the packaging after use
Figure 5 below shows the ways farmers handle pesticide packaging after they use it.
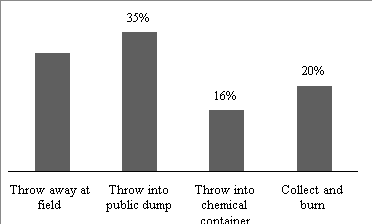
Fig. 5. Ways the farmers handle the packaging after use
The majority of households throw their packaging at the common landfill (34/99), accounting for 35 %. Currently, there are some communes where packing areas have been arranged, but the rate is low (15/99), accounting for 16 %. After being used, most of the boxes, bottles and packages of pesticides are thrown directly at the place of use. About 29 % of the farmers (29/99) were interviewed and discarded the peels after using them at the spraying site. It was very easy to find used medicine bottles and jars in the field, such as along the banks of fields, under canals or in gardens. This landfill disposal affects the landscape as well as the surrounding environment and endangers human health, which is considered a major problem, reported in many studies (Gill & Garg 2014; Osborne et al. 2015). These handling methods of farmers are not comly with the provisions of Joint Circular No. 05/2016/TTLT-BNNPTNT-BTNMT dated May 16, 2016 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development — Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment about Guidances on the collection, transportation and treatment of pesticide packaging after use.
Only a small percentage of farmers (16 %) treated it by placing it in a separate container containing chemical packaging. According to the survey, only 3/11 communes have been allocated places to put bottles, jars and packages of pesticide, the remaining communes have not yet been arranged.
In addition, the majority of farmers surveyed (88 %) washed sprayers right in the field canals or in ditches and ponds in the rice field. Wastewater from the washing of spraying equipment is dumped in the field. The rest of the people carried the washing sprayer and dumped the sewage directly in the canal. This practice has introduced pesticide residues into the water in canals, ponds and lakes and it is a source of pollution of surface water and groundwater if there is no solution to regulate and improve farmers' behavior.
3.3.6. The knowledge level of harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and human
Figure 6 shows the knowledge level of farmers about the harmful effects of pesticides on human health and the environment.
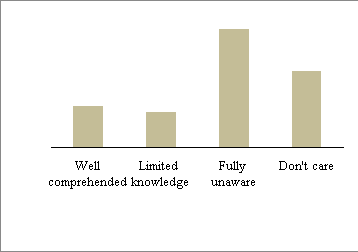
Fig. 6. The knowledge level of harmful effects of pesticides on
the environment and human
The results show that the percentage of people completely unaware of the harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and humans is as high as 44 %. The percentage of households who understand about the harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and humans is equivalent to the percentage of farmers who comprehend these harmful effects (13 % and 15 %, respectively). The percentage of farmers who don't care about the harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and humans accounted for 28 %. These results show a lack of understanding about the potential impact of pesticides on humans and the environment. This situation can be explained by the low level of education of the farmers here, with the majority having only primary and lower secondary education (65 %), 15 % reaching high school education and 8 % have never attended school.
In addition, results from the survey shows that organize training sessions by agricultural personel are rare, including ones to propagate about the harmful effects of drugs as well as provide technical instructions on how to use them properly. Only 6/11 communes have been organized but the frequency is very little once a year.
3.3.7. Farmers’ awareness/attitudes about indiscriminately disposing of pesticide bottles after use
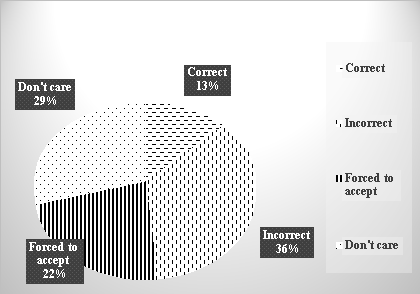
Fig. 6. Farmers’ awareness/attitudes about indiscriminately disposing of
pesticide bottles after use
While 36 % of people are aware that indiscriminate disposal is an illegal act, 22 % of people have to accept it because there is no other way since the commune has not yet arranged waste bins or sites to store pesticide bottles and packaging. 29 % of households are not interested in this issue at all and 13 % of households think that it is right to throw these bottles/ packaging into the surrounding environment, showing that a large part of households do not have enough knowledge and awareness about the proper action in pesticide packaging disposal.
3.3.8. Symtoms of farmers when exposed to pesticides
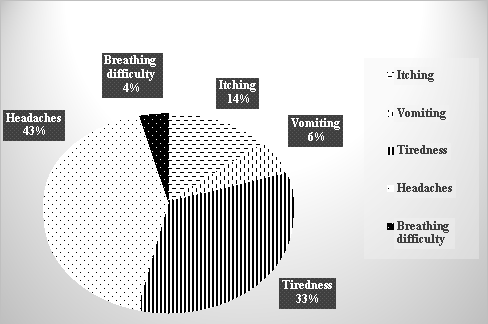
Fig. 7. Symtoms in farmers when exposed to pesticides
The most common symtoms of people exposed to pesticides are headache, dizziness accounting for 43 % and fatigue (34 %), a small part of them having symptoms of itching (14 %). Shortness of breath and vomiting, although a very small proportion, represent the harmful effects of pesticides to human health. The symptoms described by farmers in this area after exposure to pesticides are similar to some published studies such as Jensen et al. (2011); Khan et al. (2014).
3.4. Proposing solutions to manage and use pesticides more effectively and safely
The survey shows that the selection and use of pesticides, how to handle excess drugs as well as drug packaging after use were in an unreasonable and unsafe manner. To carry out these tasks more effectively and safely, some measures were proposed as below and require coordination between three groups of agencies/individuals involved, including: local management agencies, business households distributing pesticides and farmers directly buy and use pesticides.
3.4.1. For local management agencies
— Organize training sessions, propagandize people before each crop on farming techniques, the meaning of proper collection and disposal in regarding to pesticide bottles and packaging to the environment and community health, and the meaning of safe practice of pesticide application.
— Arrange storage and collection sites of pesticide packaging after use for proper disposal.
— Strengthen the inspection, examination and handling of violations in the pesticide business such as having no practice certificates or expired ones, no business license, selling drugs outside the permitted list, fake or poor quality pesticides. Strengthen supervision from the community for more effective management.
— Organize periodical mandatory training for those who are granted the certificate of pesticide business practice in order to enable pesticide sellers to master the application techniques, and to give proper and effective advice to consumers.
— Conduct periodic health checks for farmers so that they are more aware of the effects of pesticides on health and detect and treat diseases in time.
3.4.2. For pesticide businesses
The survey results have shown that people's way of choosing and using pesticides is mainly through sellers, so improving knowledge as well as checking practice certificates, checking pesticides, improving expertise subject of the business establishment is extremely necessary.
— Pesticide business should participate in training courses, further fostering professional knowledge to advise and guide buyers on how to use drugs and ask farmers to comply with the requirements listed on the packaging.
— Comply with the provisions of having a business license, types of drugs, conditions of pesticide storage to ensure requirements, quality and no drugs on the list of drugs banned from trading.
3.4.3. For farmers
3.4.3.1. Precaution management
The rate of using chemical pesticides in Phu Ninh district accounts for a large part compared to biological pesticides. Therefore, there should be biological measures to prevent pests and crop diseases in advance to minimize the abuse of chemical pesticide use:
— Using highly resistant rice varieties, rotating crops, intercropping crops, proactively preventing pests and diseases, in order to save costs and limit pesticide residues in agricultural products.
— Encourage farmers to use biological pesticides instead of chemical ones.
3.4.3.2. Measures to propagate and raise awareness for farmers
— Extensive propaganda through local media (commune, district) such as television, radio, newspapers, etc. to raise awareness of responsibilities and obligations of people who trade in and use pesticides in proper manner.
— Organize training programs on skills to use pesticides, update the list of pesticides banned from trading and use, knowledge about the harmful effects of improper use of pesticides, handling packaging after use for farmers, granting certificates and updating knowledge every year.
— Encourage people to pay attention to the origin of pesticides, to only buy products from reliable pesticide trading addresses in the reputable system, know how to choose the right types of pesticides for each type of pest and disease.
4. Conclusions
The study examines the current status of use and proposes some measures in order to limit the abuse of pesticides by people. Some main findings obtained from this survey concludes:
— Phu Ninh district has favorable natural conditions for general economic development and agricultural production, but it is also prone to pest outbreaks.
— The survey subjects were mainly elderly people with relatively low levels of education.
— Pesticides used by farmers were diverse and abundant in categories
— Farmers choose pesticides mainly based on information provided by sellers and instructions on product packaging.
— Pesticide surplus were mainly sprayed until empty or sprayed for other crops.
— Packaging and bottles of pesticides after sprayed were mainly put in the general waste bin or thrown in the field.
— The percentage of surveyed farmers in the district who do not understand the harmful effects of pesticides on the environment and human was quite high at approximately 50 %. Up to 28 % of farming households do not care about the harmful effects of pesticides.
— The most common symptoms of pesticide exposure included headache, dizziness and fatigue, in addition to rash, vomiting and difficulty breathing.
Based on the survey results, the study also proposed solutions for better management, to improve the knowledge as well as awareness of pesticide traders and farmers in using pesticides safely and effectively.
References:
- Atreya, K., Johnsen, F. H., & Sitaula, B. K., “Health and environmental costs of pesticide use in vegetable farming in Nepal”, Environment, Development and Sustainability , 14(4), 2012, 477–493.
- Chen, S., F. He, Z. Zhang, Y. Gao, A. Zhou, C. Xie, L. Xiong, D. Chen, S. Wang, and J. Jia, «Evaluation of a safety educational programme for the prevention of pesticide poisoning», La Medicina del lavoro , 89, 1998, S91–8.
- Gill, Harsimran Kaur, and Harsh Garg, «Pesticides: environmental impacts and management strategies». Pesticides-toxic aspects . IntechOpen, 2014.
- Jallow, M. F., Awadh, D. G., Albaho, M. S., Devi, V. Y., & Thomas, B. M. “Pesticide risk behaviors and factors influencing pesticide use among farmers in Kuwait”. Science of the total environment (574)2017, 490–498
- Jensen, H. K., Konradsen, F., Jørs, E., Petersen, J. H., & Dalsgaard, A., “Pesticide use and self-reported symptoms of acute pesticide poisoning among aquatic farmers in Phnom Penh, Cambodia”. Journal of toxicology , 2011, 2011.
- Jones, E., Mabota, A., & Larson, D. W., “Farmers' knowledge of health risks and protective gear associated with pesticide use on cotton in Mozambique”. The Journal of Developing Areas , 42(2), 2009, 267–282.
- Khan, K., Ismail, A. A., Rasoul, G. A., Bonner, M. R., Lasarev, M. R., Hendy, O.,... & Rohlman, D. S., “Longitudinal assessment of chlorpyrifos exposure and self-reported neurological symptoms in adolescent pesticide applicators”. BMJ open , 4(3), 2014, e004177.
- Ríos-González, A., Jansen, K., & Sánchez-Pérez, H. J., “Pesticide risk perceptions and the differences between farmers and extensionists: Towards a knowledge-in-context model”. Environmental research , 124, 2013, 43–53.
- Yamane, T., Statistic: An introductory analysis , 2 nd Ed., New York: Harper and Row, 1973.
- https://vanbanphapluat.co/thong-tu-lien-tich-05–2016-ttlt-bnnptnt-btnmt-thu-gom-van-chuyen-bao-goi-thuoc-bao-ve-thuc-vat
- Le Tam, “Some solutions to handle residual pesticide residual”, Center for analysis and transfer of environmental technology, 2016. http://phantichmoitruong.com/detail/mot-so-giai-phap-xu-ly-hoa-chat-bvtv-ton-luu.html