During the work carried out such tasks as qualify assets, determine subclasses of assets, defining threats and vulnerabilities from ISO/IEC
27002, COBIT 4.1. The knowledge model can be used to support a broad range of information security risk management approaches. The expert system analyzes the state security of some company, brings out vulnerabilities, threats, and provides with advisory information for information security. Automation of the audit process by creating intelligent software (expert system) can significantly reduce the cost, as the most important work on decision-making is carried out automatically.
Information technology is extensively used for the effective execution of business processes in commercial and government enterprises. Intensive use of such systems for the storage, processing and transmission of information has led to problems related to their protection. The rapid growth of information systems has significantly increased volumes of vulnerabilities and threats of information technology. This cause greatly stimulated the development of the information systems audit.
Information is a valuable asset for various enterprises. The influence of threats on companies in terms of financial losses is considerable. Ease of transmission, processing, storage and use of information plays a key role for enhancing the competitiveness of the enterprise.
The audit of information security conducts to improve information security, which can provide up to date information and independent assessment of the state of information security. Reducing the cost of the audit is one of the priorities of any organization. There is a need for an automated system that would issue a quantitative result, the state of information security, with appropriate advisory information. Vulnerabilities in assets deficiencies in assets, or the lack of security procedures, engineering controls and physical controls, which can be used to harm or predispose assets to harm. The benefit of information systems audit is analyzing operating system access controls, and analyzing physical access to the systems. The basic issue for various enterprises is managing security vulnerabilities and potential threats, which can be classified, evaluated and mitigated. The commercially sensitive essential information should be adequately protected, so systems audit has a significant role for organizations to ensure information security.
The intelligent system for information security auditing is relatively inexpensive, which can evaluate both threats and vulnerabilities, provide advisory information. Also there is no publicly available and widely used software for auditing information security systems. Individual consulting and auditing companies create template software to support internal and external audit, which allow reflect individual elements of systems, but there are no expert systems for information security audit.
The actuality of intelligent system for information security auditing is relatively small price and implementation in a short time, because information security audit process is expensive and time consuming process. Some phases of information security auditing can take weeks, whereas the expert system can determine it significantly reduce in comparison with a human expert. For development expert system were used international standards such as ISO/IEC
27002, COBIT 4.1, from these standards were taken basic information, which allows ensure high level of the advisory information.
The knowledge base of the information security audit expert system
ISO/IEC 27002
The ISO 27002 standard is a code of practice for information security. It substantially defines hundreds of possible controls and control arrangements, which may be implemented, in theory, subject to the guidance provided within ISO
27001. The standard «formed guidelines and common rules for initiating, realizing, supporting, and developing information security management within an enterprise». The practical management itemized in the standard is assigned to address the certain requirements matched throughout a regular risk evaluation. The standard is also assigned to keep a guide for the development of «organizational security standards and efficient security control practices and to assist make confidence in inter-organizational performance». The purposes defined guarantee common guidance on the generally taken goals of information security management. Guidance keeps best practices of control objectives and controls in the following areas of information security management:
– security policy;
– organization of information security;
– asset management;
– human resources security;
– physical and environmental security;
– communications and operations management;
– access control;
– information systems acquisition, development and maintenance;
– information security incident management;
– business continuity management;
– compliance.
COBIT 4.1
ISACA incessantly updates and expands the practical guidance and product family based on the COBIT framework. COBIT helps IT professionals and enterprise managers perform their IT governance and management commitments, especially in the areas of assurance, security, risk and control, and deliver value to the business. COBIT is an IT governance framework and encouraging toolset that lets managers to cover the gap between control requirements, technical is- sues and business risks. COBIT permits comprehensible policy development and good practice for IT control throughout organizations. COBIT underlines control compliance, helps organizations to increase the value attained from IT, permits adjustment and simplifies realization of the COBIT framework. CO- BIT covers good practices across a domain and process framework and performs actions in a manageable and logical structure. COBIT’s good practices deliver the agreement of experts. It is focused more on control and less on implementation. These practices will help optimize IT-enabled investments, ensure service delivery and provide a measure on which to judge when things do go wrong. The main task for any organization is achieving appropriate management and control of IT. COBIT is focused on this high level process which requires suit- able management and control. COBIT is concentrated on what is required to achieve adequate management and control of IT, and is positioned at a high level. COBIT has been balanced and coordinated with other IT standards and practices. The process focus of COBIT is illustrated by a process model that subdivides IT into four domains and 34 processes.
The identification of recommendations
An analysis of the classification of assets were identified (Figure 1), subclasses attributes of assets, were identified threats from Threats Catalogue — Elementary Threats, were established vulnerabilities and controls from ISO/IEC
27002 Information technology — Security techniques — Code of practice for information security management and COBIT Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology. One of the line entries on your balance, intangible assets are probably one of the hardest items to put an actual value to and are only recorded on the balance sheet if purchased and are ignored if internally generated. They’re reviewed annually and written down if their value is deemed to have been impaired. For example, doesn’t represent any measurable asset. It’s simply the premium paid over and above the net value of the assets in the acquisition of a company. Goodwill presumably reflects the value of things such as employee talent, market reputation and technology. Until just a few years ago, goodwill was amortized over time. The accounting changed so that goodwill stays on the books for the original amount unless the fair value of the acquired assets is judged to be «impaired.» If purchased, they are carried for the purchase price. However, the research and development costs of internally generated patents, no matter how valuable, are expensed as they occur.
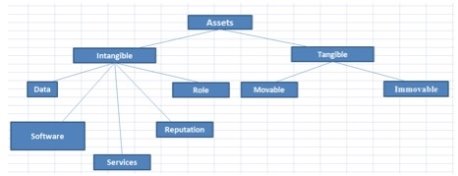
Figu. 1. Classification of assets
Here is an example from ISO/IEC 27002, the section 11 — Access control (ISO/IEC 27002) is about how should be established access to information, information processing facilities, and business processes should be controlled on the basis of business and security requirements. The subparagraph 11.2 Users access management, here is described the formal procedures to ensure authorized user access and to prevent unauthorized access to information systems.
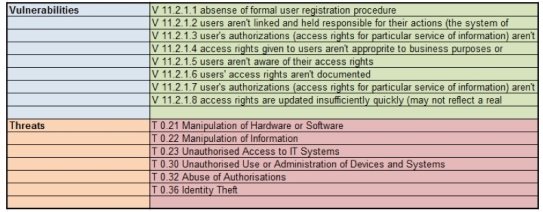
Fig. 2. Identified vulnerabilities and relevant threats
The manipulations should spread all stages in the life-cycle of user access, from the initial registration of new users to the final de-registration of users who no longer require access to information systems and services. Special attention should be given, where corresponding, to the need to control the allocation of privileged access rights, which allow users to override system controls. Access control rules should take account of roles for information authorization.
Table 1
Appropriate management practices and recommendations.
|
ISO/IEC 27002 |
COBIT 4.1 |
IT processes(COBIT 4.1) |
|
11.2.1 User registration |
DS8.1 Service Desk DS8.2 Registration of Customer Queries DS5.3 Identity Management DS5.4 User Account Management |
DS8 Manage Service Desk and Incidents DS5 Ensure Systems Security |
Conclusion
Application of the proposed method allows you to create an expert system that allows you to give a qualitative assessment in the process of information security audit, and avoid the need to perform extensive testing, since the audit of information security is a time-consuming process that can last for several months, which can be costly. Therefore, the application of the proposed method can not only speed up the time of the audit, but also reduce the cost of auditing information security.
References:
- ISO/IEC 27002 «Code of practice for information security management»
- COBIT Objectives for Information and Related Technology»
- Stepanova, D. Parkin, S. and Mursel, A. 2009. The knowledge base of information security decision making. 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies (ICSOFT 2009), 326–311.

