The relevance of the topic: Varicose disease of the feet is due to hormonal and neuroendocrine changes that occur much during pregnancy, and in 40, 5 % of pregnant women tripled. Thromboembolic complications from the varicose disease in developed countries are the main cause of maternal mortality. Thromboembolic complications in obstetrics are three out of 1000 pregnancies. The varicose disease of the lower parts of the body in pregnant women leads to a decrease in the quality of life of a woman and an increase in maternal mortality as a result of complications during pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum period. Despite the abundance of methods of treatment, it is not used during pregnancy. In the complication of the disease, the relapse of the disease, complications, extiogenesis of the disease were reduced through operative cross-sectional surgery (Troyanov-Trendelenburg).
The purpose of the study : to optimize the methods of treatment of migratory thrombosis in pregnant women with the varicose disease and to reduce complications.
Material and methods: 47 pregnant women with varicose veins of the legs treated in 2017–2020 at Samarkand Regional perinatal Center were studied. They were followed by General examinations, a doplerometry examination, an angiologist, and therapist examinations.
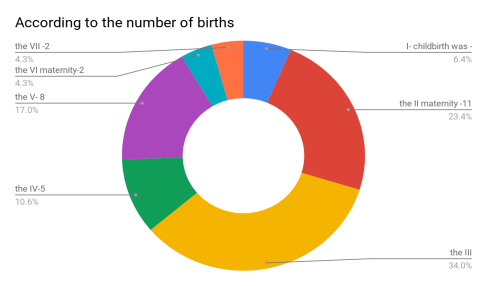
Results: The mean age of the pregnant women was 25–32 years. In all of the examined patients — 47 (100 %) had a history of pregnancy against a background of anemia. According to the course of childbirth: operative childbirth (fractional cutting) was 43 (91,4 %), childbirth by natural means was observed in 4 (8,6 %) AEL. According to the duration of complications, there were 13 (27,6 %) severe cases, while the remaining 34 (72,4 %) women had normal complications. According to the number of births, I- childbirth was -3 (6,4 %), the II maternity -11 (11,4 %), the III — 16 (34 %), the IV-5 (10,6 %), the V- 8 (17 %), the VI maternity-2 (4,25 %), the VII -2 (4,25 %).
According to the complication of the gestational period: with the risk of miscarriage of the fetus — 4 (8,5 %), multiple — 3 (6,4 %), low — wateriness — 1 (2,1 %), fetoplacental insufficiency — 3 (6,4 %), pathology of placenta attachment — 5 (10,6 %), chronic pyelonephritis — 6 (12,8 %), preeclampsia — 2 (4,25 %), prenatal course of papillomavirus — 4 (8,5 %), gestation hypertension — 3 (6,4 %), premature migration of the normally located placenta — 3 (6,4 %), obesity — 3 (6,4 %), thrombophlebitis — 3 (6,4 %), hernia-2 (4,25 %) complications in a woman.
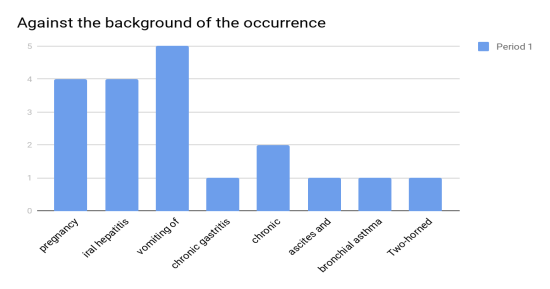
Against the background of the occurrence of pregnancy occurred 4 (8,5 %), viral hepatitis — 4 (8,5 %), vomiting of pregnant women 5 (10,6 %), chronic gastritis — 1 (2,12 %), chronic cholecystitis — 2 (4,25 %), ascites and anasarca — 1 (2,12 %), bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis-1 (2,12 %). Two-horned uterus 1 (2,12 %) met in the fetus.
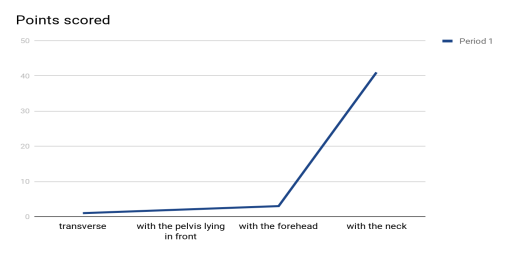
According to the location of the fetus: transverse — 1 (2.12 %), with the pelvis lying in front — 2 (4.24 %), with the forehead — 3 (6.36 %), with the neck — 41 (87.3 %) formed.
According to the number of fetuses: twins — 1 (2.12 %), triplets — 1 (2.12 %), singles — 45 (95.76 %). Antenatal mortality due to complications was 1 (2.12 %), hysterectomy with uterine excess was 1 (2.12 %), and maternal mortality due to OATE and migratory thrombophlebitis was 1 (2.12 %).
Crossectomy (Troyanov-Trendelenburg operation) was performed under endotracheal anesthesia in 8 (17 %) of the examined pregnant women. The duration and recurrence of the disease increased in 44 (93.6 %) patients as the pregnancy progressed. Skin changes in varicose veins of the legs in 17 % of 8 patients were observed hyperpigmentation and lipodermatosclerosis. Patients were studied in 2 groups. Complications of the disease were obvious in group 1 patients, such as varicothromboflebitis, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary artery thromboembolism. In group 1 patients it was 4–6 days, in group 2 it was 8–9 days. No relapse was observed in patients of the first group, in group 2 patients — was used simultaneously with. In group 2 patients, only heparin therapy was performed after delivery without surgery. Recurrence was observed in 8 patients (17 %) when 1 heparin therapy was used without surgical treatment on the day of bed rest. When 100 % of the patients in the main group underwent operative treatment with heparin therapy, there were no complications of relapse of the disease, varicotromboflebitis, and deep vein thrombosis pulmonary artery thromboembolism. In the postpartum period, the use of heparin therapy received complications of acute migratory varicotromboflebitis. In the comparative group, relapse was observed in 6 (15.4 %) patients.
Conclusion: Most of the methods of treating varicose disease during pregnancy are contraindications. Heparin therapy, which was used in combination with surgery for the Prevention of complications, a decrease in the days in the hospital, a decrease in the extirpation of drugs, relapse, complications caused by pregnancy, varicotromboflebitis, deep vein thrombosis, a decrease in the mortality of mothers as a result of complications of pulmonary artery thromboembolism, is the most basic treatment during pregnancy.
References:
- Dijkstra ML, Khin NY, Coroneos JC, Hazelton S, Lane RJ. The effect of pregnancy on venous valve repair to the sapheno-femoral junction for varicose veins // Obstet Med. 2014;7(2): 84–9.
- Gavrilov S. G. Varicose veins of the pelvic vein: when and how to treat // Phlebology. — 2007; 1: 9–12.
- Ikhtiyarova G. A., Dustova N. K. Early diagnosis of complications of varicose veins in pregnant women // Monograph 2018; Latvia — 32.
- Jawien A. The influence of environmental factors in chronic venous insufficiency //Angiology. -2003.-V. 54.-Supp. 1.- P. 19–31.
- Lim CS, Davies AH. Pathogenesis of primary varicose veins // Br J Surg. 2009;96(11):1231–42.
- Manzhula L. V. The effect of treatment of varicose veins during pregnancy and after childbirth on obstetric and perinatal delivery outcomes // Woman's Health 2013; 8(84): 108–110.
- Акушерство. Национальное руководство /под ред. Э. Е. Айламазяна, В. И. Кулакова, В. Е. Радзинского, Г. М. Савельевой -М.: ГЭОТАР- Медиа. -2008.-1200с.
- Акушерство: национальное руководство. Под ред. Айламазяна ЭК, Кулакова ВИ, Радзинского ВЕ, Савельевой ГМ. Москва, РФ: ГЭОТАР-Медиа; 2007. 1200 с.
- Безнощенко ГБ, Кравченко ЕН, Цуканов ЮТ, Кропмаер КП, Цыганкова ОЮ. Варикозная болезнь у беременных: особенности гестационного периода, флебогемодинамика малого таза и нижних конечностей. Российский вестник акушер-гинеколога. 2016;16(3):4–8.
- Горелик С. Г., Литынский А. В., Поляков П. И. Варикозная болезнь нижних конечностей, особенности у лиц старших возрастных групп // Fundamental research. 2012. № 5. С. 276.
- Джобава ЭМ, Степанян АВ, Панайотиди ДА, Болкунова НВ, Доброхотова ЮЭ. Особенности течения, диагностики и терапии плацентарной недостаточности при варикозной болезни. // Акушерство, гинекология, репродукция. 2011; 5(4): 13–9.
- Доброхотова Ю. Э., Джобава Э. М. Плацентарная недостаточность.Современная терапия.Особенности течения плацентарной недостаточности при варикозной болезни /М: Издательство «Адамант ". — 2011.-32с..
- Иванов Е. В., Низамов Ф. Х., Мизайлова А. В. Течение беременности и родов у женшин, страдающих варикозной болезьню нижних конечностей // Медицинская наука и оброзавание Урала. 2012;13(71):5–7.
- Камилова М. Я., Рахматуллаева Д. М., Ишан-Ходжаева Ф. Р. Медицинские и социальные факторы развития плацентарной недостаточности у беременных женщин в современных условиях Таджикистана. //Журнал акушерства и женских болезней. — 2015.-Том LXIV — Вып. 6.- С 26–30.
- Камилова М.Я, Касымова Ш. С. Особенности течения беременности и перинатальные исходы у женщин с варикозной болезнью // Вестник Авиценны. 2016; 3: 47–51.
- Abdurakhmonov M. M., Khodzhaeva N. B., Dustova N. K. Etiology of varicose veins of the small pelvis during pregnancy // International scientific journal «Problems of Biology and Medicine» Samarkand 2012; 1(68): 154–156.

