The article examines integrate information flows Enterprise Resource Planning software system and blockchain across the entire set of supply chain disciplines and processes for automotive plants. Automotive builders are facing a strong, worldwide competition. Consequently they have to reinvent their market approach and expand their business. Changing the focus from the selling price optimisation to the life cycle cost optimisation could lead to competitive advantages and enable new business opportunities. The original blockchains were entirely public (BitCoin and Ethereum), and that's not ideal for most enterprise automotive industry business transactions. But blockchains alone cannot ensure the authenticity of automotive spare parts goods for automotive plants. Crypto labels reader for cryptographic label technology or cryptographic label systems will help solve the blockchains problem.
Keywords: blockchain, cryptographic, labels, reader, technology, automotive, software.
The automotive industry is undergoing the most significant change. Automotive companies of today are not just creating new products and services. Through the global supply chain, spare parts for car's often change hands repeatedly before reaching their destination automative plant. Non-traditional automotive companies are entering the industry, bringing technologies and new services that are disrupting current business models. Automotive original equipment manufacturers will gain real-time analytics on performance design verses actual use. Automotive companies are increasingly integrating their core business functionalities with third parties and their platforms. For the first time, major rivals are collaborating to design future value chains that transform businesses, products and even the market itself. Automotive leaders will use these relationships to reshape their organizations for growth in a digital world.
Leveraging blockchain is not about replacing well-established forms of supply chain interactions, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software systems, for example, SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics NAV or IFS. Rather, as organizations implement new supply chain technologies, for example Internet of Things (IoT) technologies for improved logistics processes monitoring, blockchain will be used provide a synthesized record of information flows.
This level of shared visibility will offer automotive plant an opportunity to optimize multi-party supply chain processes automotive spare parts for car’s.
As blockchain evolves and organizations increasingly adopt the technology, blockchain-based smart contract technology will be deployed to further streamline exception handling and introduce new forms of supply chain process automation. But blockchains alone cannot ensure the authenticity of goods automotive spare parts. Counterfeits can be introduced at any point along the way. Crypto Labels Technology (CLT) or Crypto Labels System (CLS) for blockchain technology is poised as the future of digital transactions, infusing trust, efficiency and transparency into supply chains automotive spare parts for automative plant. CLT will help solve the blockchains problem. Changing the focus from the selling price optimization to the life cycle cost optimization could lead to competitive advantages and enable new automotive business opportunities.
Main part
A modern cars, is composed of hundreds of thousands parts. Due to regulation, each part is tracked, and when maintenance is performed, that work must be logged. The problem is that every entity in the maintenance chain, from automotive plant operator and maintenance group to the parts suppliers and regulators, is often on disparate software systems. Even when they use integrated systems, communications may not be standardized and could be verbal or paper-based, leaving many single points of failure in tracking operations. For the automotive industry, blockchain offers consensus among parties, provenance of data, immutability and finality. As the blockchain continues to mature and find adoption in areas other than cryptocurrency, ERP vendors are working to integrate the distributed ledger technology as a trackable, immutable record for everything from shipping manifests and supply chains to equipment maintenance and dispute-resolution systems. The value achieved through integrating blockchain with ERP systems comes not by creating and porting new information into the distributed ledger, but by drawing existing data from enterprise systems and being able to tightly control with whom it is shared. Blockchain will not replace ERP systems, but be a complementary application that can simplify integration between parties and reduce vulnerability because of its innate security. Building sophisticated tools for managing privacy and security while sharing information selectively is key for enterprise adoption at scale. While we see companies eventually wanting to use public blockchains for their business operations, most early implementations will be private blockchains where it is easier to control and manage privacy and security. What won't be difficult is integrating blockchain with ERP systems. A huge role for product identification for through life asset management and blockchain technologies be played by CLT. The CLT has two main elements: crypto labels reader and crypto labels (CL).
The CLR [1] (see Fig.2) contains a Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Scanner and NFC (Near Field Communication) Reader built-in smartphone, for example Apple iPhone 6/7/8.
NMR Scanner for authenticating and/or identifying of Crypto Labels for space, aviation, automotive, defense devices comprise a units generating either continuous or pulse, either modulated or non modulated emitted radiation in the radio frequency band, including a generator of continuous or pulse modulated or non modulated radio frequency signal and an emitting probe head or coil, transforming it into electromagnetic radiation, and a system for detection of the re-radiation emitted by the resonant substance in response to the radio frequency radiation, including receiving probe head or coil and detection device with a registration device determining presence of the re-radiation from the resonant substance.
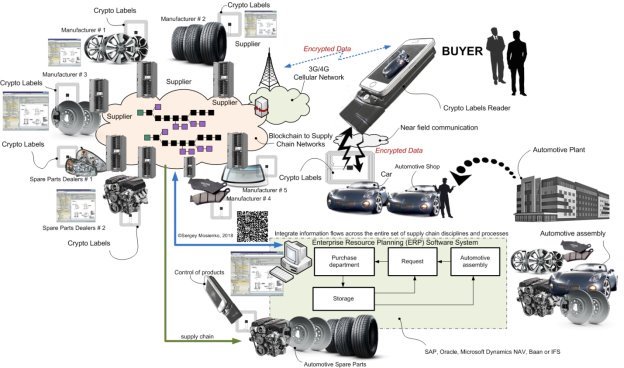
Fig. 1. Automotive using ERP-system and blockchain
СL’s [2] (see Fig.3) consist the NFC-chip or secure smart card controller, smart card controller antenna and magnetic resonance metal-transponder at insulation on which materials are deposited nuclear magnetic resonance in ferromagnets, or antiferromagnets, or ferrimagnets, or nuclear quadrupole resonance, or very low field electron spin resonance, or said resonance phenomenon is due to electric/magnetic dipole or tunnel transitions between Stark-Zeeman sub levels, or any combinations or aforementioned phenomena.
СL’s, tamper-proof digital fingerprints, to be embedded into automotive spare parts, and linked to the blockchain. These fingerprints can take many forms such as tiny NFC-chips, but when they are tied to a blockchain, they represent a powerful means of proving a automotive devices authenticity. These crypto labels pave the way for new solutions that can combat fraud and protect consumers or automotive plants.
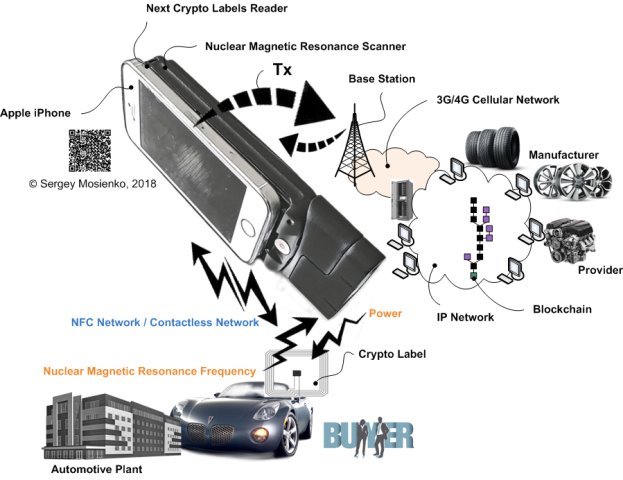
Fig. 2. Crypto labels reader
The smartphone transmits the information data received from the Crypto Labels via the base stations of the cellular network to the distributed database servers blockchains technology. The blockchain gives internet users the ability to create value and authenticates digital information crypto labels. Developing digital identity standards is proving to be a highly complex process.
Technical challenges aside, a universal online identity solution requires cooperation between private entities and government. CLR for cryptographic label technology will help solve the blockchains problem.
Conclusions
It is evident that the blockchain technology business model concept could provide benefits for the automotive plants and create a win-win situation. Cryptographic label technology or CLS will help solve the blockchains problem. Blockchain will not replace ERP systems, but be a complementary application that can simplify integration between parties and reduce vulnerability because of its innate security.
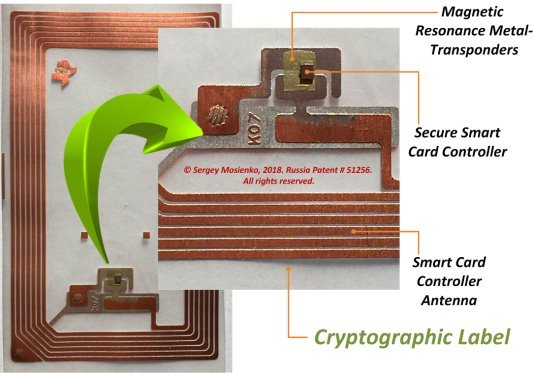
Fig. 3. Crypto label
References:
1. Patent of the RU No.72592 — Modern Identification Wireless Reader./Mosienko S. A.
2. Patent of the RU No.51256 — Protected from fake non-contact smart card microcontroller./Mosienko S. A.

