Information technology is the collection, processing, transmission, reception of information in the field of research and work with them. The pedagogy of information is collected, researched, processed and transmitted to students and groups [1,5].
A full-featured electronic textbook (ET) consists of several main parts (Figure 1.), which include:
– The main part, which describes the content of the subject presented in the form of hypertext with graphic illustrations and possibly audio and video clips;
– The test piece, which includes quizzes, exercises and tasks for the practical development of the material and self-testing, together with recommendations and examples of assignments;
– Dictionary;
– Frequently asked questions and prepared answers to them;
– Description of laboratory work, if the curriculum such work are provided, including the original software to perform these works [1,5].
The main part of ET usually either represented as a combination of lectures (lessons), or structured with the release of sections, chapters, sections of books like building a traditional form. It is also possible to build modular power plant with capacity of operational text compilation of set of power plants available modules, implemented in interactive electronic technical manuals (IETM) and in electronic applications encyclopedias [2,4]. The test piece can be centered or in a book of problems, or distributed by sections and chapters of the main text, or expressed in the aggregate of test modules [3,5].
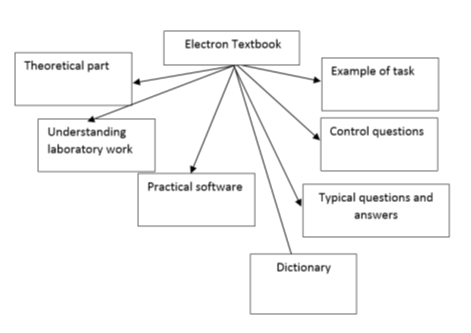
Fig. 1. Structure of full-featured electronic textbook
Explanatory Dictionary of terms is in the form of hyperlinks to the relevant part of the basic place and brief definitions of these terms (and sometimes definitions may be missing) [3,4,5]. There are three ways in laboratory work. The first of these is the traditional, it is based on a real (physical) laboratory equipment, located in the training center with the attendance of students in the center [4,5]. To this end, training plans and schedules of people trained by remote technology, the special session should be allocated. The second method is also based on the use of physical equipment, but with remote access to it with the help of telecommunication technologies and special software and hardware [3,5]. A third method involves the execution of computer experiments in virtual labs using mathematical models implemented in the appropriate software.
In the description of the laboratory work should be included, in addition to the necessary theoretical material, or links to it, and review questions, information about your hardware, software and hardware, setting and presentation of results [4].
By e-learning materials are presented both traditional and specific requirements arising from the possibilities of information technology. Among the main characteristics of teaching materials, which are subject to the traditional requirements, there are the following properties [4]:
– completeness of the presentation, defined as the line adopted curriculum subjects;
– Availability of presentation that will be mapped to the pre-treatment level of contingent of students, for which the material is intended;
– •scientific content, that the content reflects the current state and recent developments in the relevant scientific field;
– •the logic and consistency of presentation.
Fig. 2.Testing on the subject «Organization of e-government network»
Learning Object Metadata (LOM) — System of metadata descriptions of educational resources, the proposed IEEE LTSC and used by IMS. LOM metadata defines the following categories:
1) general category combines information about the educational facility as a whole;
2) category of the life cycle includes elements of the history and current state of the learning object and those who influenced him in the course of evolution;
3) category of meta-metadata contains information about the metadata;
4) Technical category groups the technical requirements and characteristics of the learning object [5];
5) the educational category combines educational and pedagogical characteristics;
6) The category of rights includes data on intellectual property and conditions of use;
7) category of relations (correlations) defines the concepts that define the relationship between this and other educational facilities;
8) category annotation comments to the educational use of the object and details about the creators of these comments;
9) classification category determines the location of the object in the space of a classification scheme.
Collectively, these categories form the basic scheme LOM. With the use of the classification categories are various types of extensions of the scheme [5].
References:
- Abdukadyrov, Abdukahhor Abduvakilevich. Masofali ukitish nazariyasi amaliyoti Islands. Monograph / AA Abdukadir, AH Pardaev; Ed. M. Sodikova. — T: Uzbekistan Respublikasi fanlar Akademiyasi «FAN» nashriёti, 2009. — 145 p.
- Masofadan ukitish equipment wa tehnologiyasi. — T: TEAI, 2002. — 232 b. — (Halkaro ilmy — Amal Conference Maruzalar tuplyu yil 2002 May 13–14: Uzbek-mail wa agentligi telecom «Uzbektelecom» aktsiyadorlik Kompaniyasy Uzb Radiotekhn electron Islands aloka ilmy and Technical Zhamiyati Tosh electrotechnical aloka in-ti). — 2 copies.
- Theory and practice of distance education. Proc. allowance for students. universities, teaching. on ped. specialist. / Ed. prof. ES Polat. — Moscow: Academy, 2004. — 416 p. — (Higher Education prof..).
- Electronic means of distance learning VZFEI: electronic supplement to the journal «Computer teaching programs and innovation». Vol. 2. — M.: VZFEI, 2005. — 1 CD-ROM. — 1 copy. — B. c.
- Information technology and distance learning tools.: Proc. Benefit / IM Ibragimov; Ed. EV Roslyakova. -. 3rd ed. — M.: Publishing house. center «Academy», 2008. — 336 p. — (Higher Education prof..).

